Introduction To Planning
Introduction to Planning: The purpose of planning is to find a sequence of actions that achieves a given goal when performed starting in a given state. In other words, given a set of operator instances (defining the possible primitive actions by the agent), an initial state description, and a goal state description or predicate, the planning agent computes a plan.
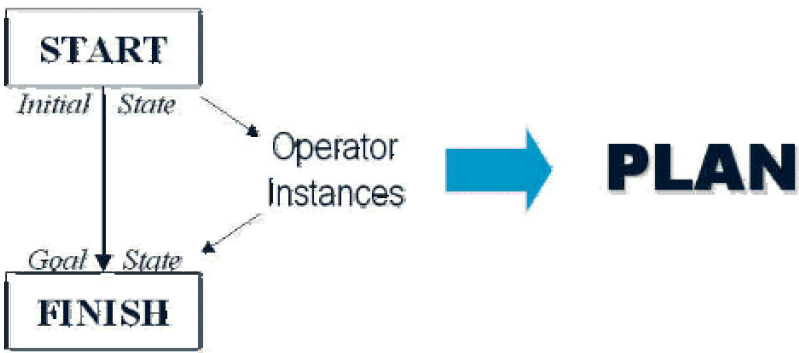
What is a plan? A sequence of operator instances, such that "executing" them in the initial state will change the world to a state satisfying the goal state description. Goals are usually specified as a conjunction of goals to be achieved.
A Simple Planning Agent: Earlier we saw that problem-solving agents are able to plan ahead - to consider the consequences of sequences of actions - before acting. We also saw that a knowledge-based agents can select actions based on explicit, logical representations of the current state and the effects of actions. This allows the agent to succeed in complex, inaccessible environments that are too difficult for a problem-solving agent
Problem Solving Agents Knowledge-based Agents = Planning Agents
In this module, we put these two ideas together to build planning agents. At the most abstract level, the task of planning is the same as problem solving. Planning can be viewed as a type of problem solving in which the agent uses beliefs about actions and their consequences to search for a solution over the more abstract space of plans, rather than over the space of situations
Algorithm of a simple planning agent:
1. Generate a goal to achieve
2. Construct a plan to achieve goal from current state
3. Execute plan until finished
4. Begin again with new goal
The agent first generates a goal to achieve, and then constructs a plan to achieve it from the current state. Once it has a plan, it keeps executing it until the plan is finished, then begins again with a new goal.
This is illustrated in the following pseudocode:

Functions:
STATE-DESCRIPTION: uses a percept as input and returns the description of the initial state in a format required for the planner. IDEAL-PLANNER: is the planning algorithm and can be any planner described in these notes or chapter 11. MAKE-GOAL-QUERY: asks the knowledge base what the next goal will be.
The agent in the above algorithm has to check if the goal is feasible or if the complete plan is empty. If the goal is not feasible, it ignores it and tries another goal. If the complete plan was empty then the initial state was also the goal state.
Assumptions:
A simple planning agent create and use plans based on the following assumptions:
- Atomic time: each action is indivisible
- No concurrent actions allowed
- Deterministic actions: result of each actions is completely determined by the definition of the action, and there is no uncertainty in performing it in the world.
- Agent is the sole cause of change in the world.
- Agent is omniscient: has complete knowledge of the state of the world
- Closed world assumption: everything known to be true in the world is included in a state description. Anything not listed is false