Air Brake System
Introduction:
Force can also be multiplied by the use of air to gain a further mechanical advantage. Everyone has felt the force of air on smaller space than that amount of air normally would occupy. For instance, air is compressed in tires to support the weight of a vehicle. The smaller the space into which air is squeezed, the greater the air’s resistance will be to being squeezed. This resistance creates pressure, which is used to gain mechanical advantage. If a constant supply of compressed air were directed through a pipe that was one inch square, and if a one inch square plug were placed in the pipe, the compressed air would push against the plug. Holding a scale against the plug would register how many pounds of force were being exerted by the air against the plug.
Construction and working of Air Brake System:
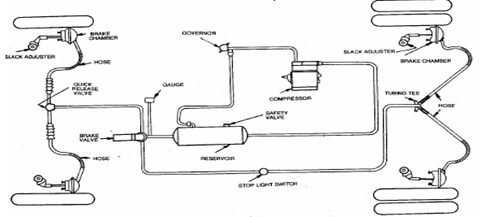
- The air brake system consists of two-stage air-compressor driven by the crankshaft or gearbox shaft. It takes air from atmosphere, compresses it and delivers to the air reservoir through un-loader valve.
- Where the pressure of the reservoir reaches the maximum degree, the un-loader valve opens to the atmosphere. Then the compressed air is directed in to the atmosphere directly.
- Each of the four wheels fitted with brake chambers consists of a diaphragm, and which the air pressure is applied and pushes it. This force operates the cam actuating lever and applies the brake.
- Each of the brake chambers is connected to the brake pedal, and air filter is also fitted between the brake valve and reservoir.
Working:
- When the brake pedal is pushed the brake valve opens and compressed air is allowed in to the brake chamber. The brake valve consists of three passages.
1. Air intake 2. Exhaust 3. Brake chamber
- When the brake pedal is pressed the exhaust passage will be closed and Air intake passage open and compressed air goes back to the chamber.
- During return stroke the exhaust passage opens while intake closes and used air goes to the atmosphere.
- This system fitted with an emergency mechanical brake, which can be used when air supply fails the air brake system, which is called air assisted hydraulic braking system.
Advantages:
1. This system used in heavy vehicles because they are more powerful than hydraulic or mechanical brakes.
2. It simplifies the chassis design
3. The compressed air is used for purposes like tyre inflation; for horn, windscreen wiper etc.
Disadvantage:
- If there is any leakage in passage the entire system will be fail.
- Therefore sealing of air is very difficult.