Alternator
Introduction:
“An alternator generates alternating current (AC) unlike a dynamo which generates direct current (DC)”.
Modern automobiles which require more electric loads are fitted with alternators instead of dynamos. These vehicles require more electrical power because they have power steering, power windows, electrical system for automobile transmission, etc.
A rectifier is required to convert AC to DC as all electrical equipment use DC.
Principle
- The principle of working of alternator differs from that of dynamo in the manner in which the conductor and magnetic field move relative to each other. In an alternator the conductor remains stationary but the magnetic field is rotated.
- However, conductor rotates and magnetic field remains stationary in case of a dynamo.
- In an alternator, a rotating bar magnet produces magnetic field which is cut by a stationary conductor.
- The north pole of rotating magnet is shown at top and south pole at the bottom.
- If this magnet is rotated by half revolution such that North Pole comes down and south pole takes upper position. During this the current in the upper leg of conductor flows in one direction.
- When the magnet is now rotated by another half revolution, the direction of current in the wire is reversed. Therefore, with the revolution of magnet, the current reverses its direction after each half revolution. Thus, an alternating current flows. This is the principle of working of an alternator.
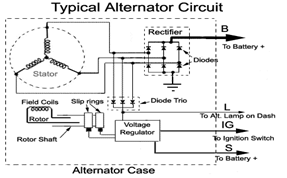
Regulators for Alternator
A regulator controls the current and voltage produced by the alternator. It is provided to prevent alternator to generate excessively high voltage.
- The battery is charged by the current generated by the alternator. For this, the battery is connected to the stator of the alternator through a diode.
- Diode allows flow of current from stator to battery but it prevents the flow of current from battery to stator when alternator is not working. Thus, it prevents discharging of battery back. Therefore, diode acts as regulator. It is put inside the alternator.
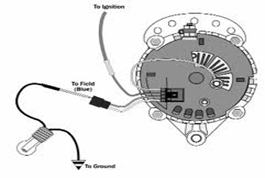
Transistorized Regulators
Some regulators, e.g. transistorized regulators are placed outside the designed. These regulators are designed to prevent the problem of damage of contact breaker points.
- As contact breaker points used I other regulators, are required to open several times in a second, they have reduced working life.
- To get rid of this problem transistors are used as switches which can be actuated by very small currents. Thus, the life of contact points is increased due to reduced arcing on account of reduced current.
- If whole circuit A is based on transistorized regulators, the system has no moving parts.