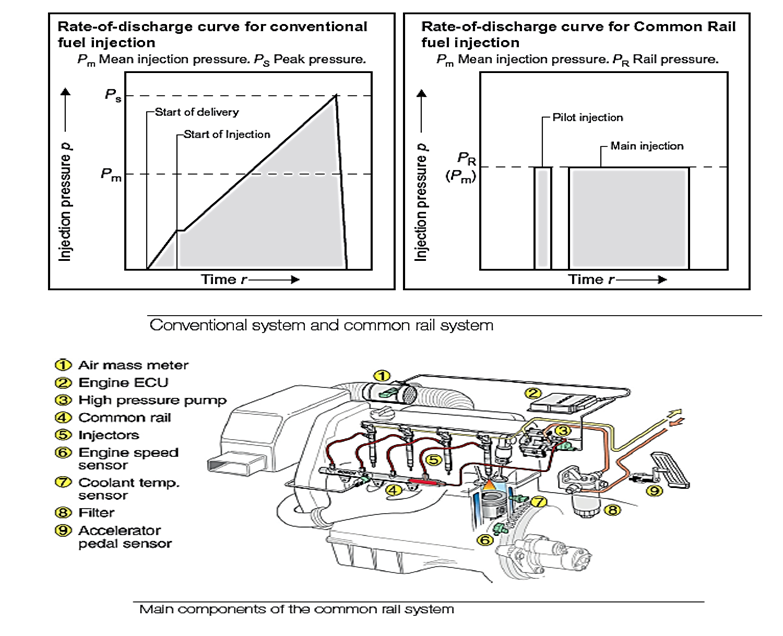
←
Automobile Engineering
Common Rail System
Introduction:
The development of diesel fuel systems is continuing, with many new electronic changes to the control and injection processes. One of the latest developments is the common rail (CR) system, which operates at very high injection pressures. Also has piloted and phased injection to reduce noise and vibration.
Components of the common rail system:
The combustion process, with common rail injection, is improved by a pilot injection of a very small quantity of fuel, at between 40° and 90° BTDC.
- The development of diesel fuel systems is continuing, with many new electronic changes to the control and injection processes.
- One of the latest developments is the common rail (CR) system, which operates at very high injection pressures. It also has piloted and phased injection to reduce noise and vibration.
- The common rail system has made it easier for small high-speed diesel engines to have all the advantages of direct injection.
- These developments have resulted in significant improvements in fuel consumption and performance. The combustion process, with common rail injection, is improved by a pilot injection of a very small quantity of fuel, at between 40° and 90° before top dead centre (BTDC).
- This pilot fuel ignites in the compressing air charge so that the cylinder temperature and pressure are higher than in a conventional diesel injection engine at the start of injection.
- The higher temperature and pressure reduce ignition lag to a minimum, so that the controlled combustion phase during the main injection period is softer and more efficient.