←
Automobile Engineering
Constantly Variable Transmission
Introduction:
The constantly variable transmission (CVT) uses a pair of cone-shaped pulleys connected by a metal belt. The key to the operation of a CVT system is a high-friction drive belt.
GENERIC ELECTRONICALLY CONTROLLED AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (ECAT):
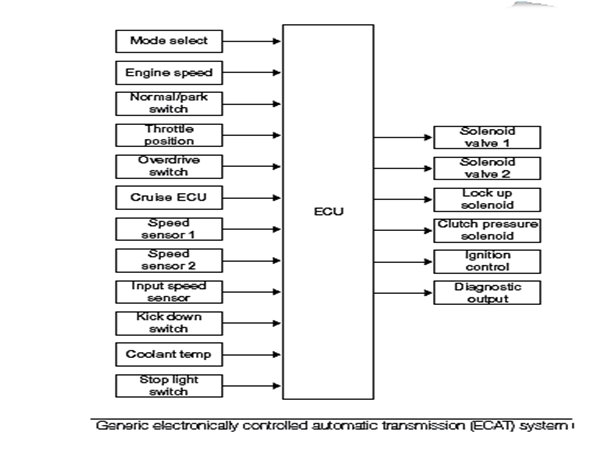
- The belt, made from high performance steel, transmits drive by thrust rather than tension.
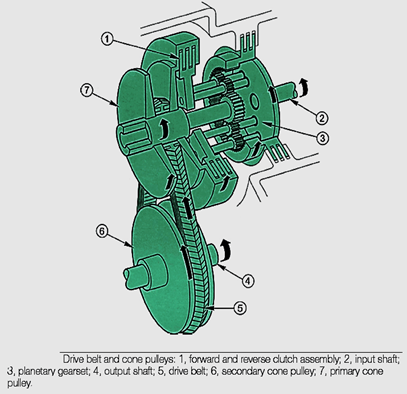
- The ratio of the rotations, or the gear ratio, is determined by how far the belt rides from the centres of two pulleys.
- The transmission can produce an unlimited number of ratios. As the car changes speed, the ratio is continuously adjusted.
- Cars with this system are said to use fuel more efficiently than cars with set gear ratios.
- In the gearbox, hydraulic control is used to move the pulleys and hence change the ratio.
- To achieve forward and reverse, a standard epicyclic gear set is used.
The drive belt transmits torque from the primary cone pulley to the secondary cone pulley unit. The belt is V-shaped and consists of several hundred steel elements held together by steel strips.