Corrective Maintenance
Introduction
Corrective maintenance is a key aspect of automobile engineering, focusing on repairing or replacing components after they have failed or malfunctioned. Unlike preventive maintenance, which aims to prevent issues before they occur, corrective maintenance deals with addressing problems as they arise. This chapter explores the principles, strategies, and best practices for effective corrective maintenance in automobiles.
What is Corrective Maintenance?
Corrective maintenance refers to the activities involved in repairing or replacing components that have failed or are not functioning correctly. The primary goal is to restore the vehicle to its optimal operating condition after a fault has been detected.
Key Characteristics:
- Reactive Nature: It occurs after a fault or breakdown has been identified.
- Focus: Aims to fix issues to bring the vehicle back to a fully operational state.
- Scope: Can range from minor repairs to major overhauls, depending on the severity of the fault.
Importance of Corrective Maintenance
Effective corrective maintenance is crucial for several reasons:
- Minimizes Downtime: Quick repairs reduce the time a vehicle is out of service.
- Ensures Safety: Addressing faults promptly helps maintain vehicle safety and reliability.
- Prevents Secondary Damage: Timely repairs can prevent further damage to other components.
- Maintains Performance: Ensures that the vehicle continues to perform optimally.
Common Issues Requiring Corrective Maintenance
1. Engine Problems
- Symptoms: Poor performance, knocking noises, or excessive smoke.
- Solutions: May involve repairing or replacing components such as pistons, crankshafts, or timing belts.
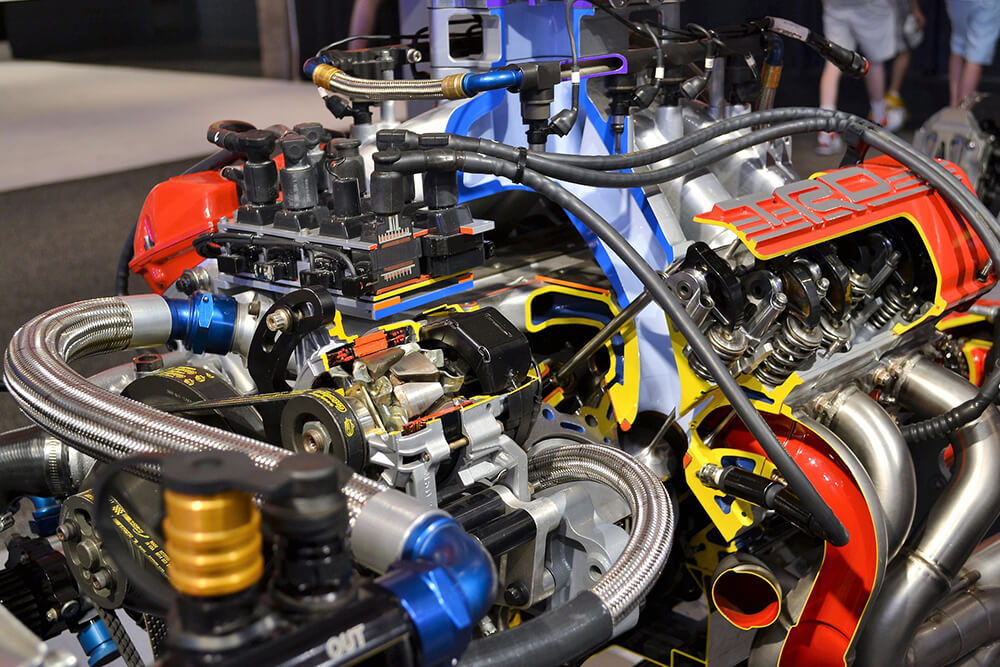
Figure: Engine Repair Process
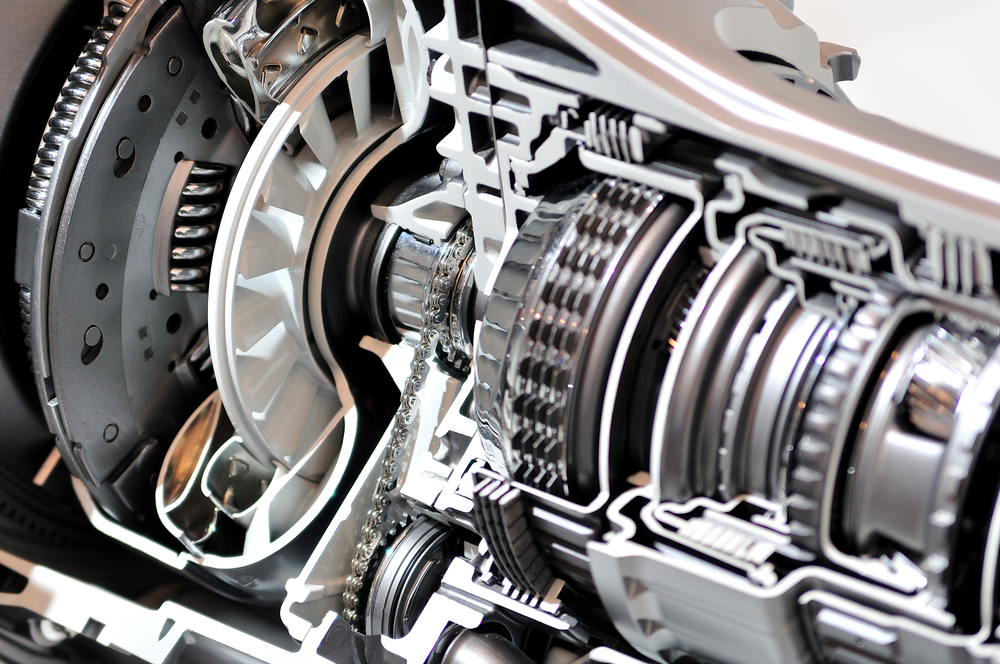
2. Transmission Failures
- Symptoms: Slipping gears, harsh shifting, or transmission fluid leaks.
- Solutions: May include transmission fluid replacement, clutch repairs, or complete transmission overhauls.
3. Brake System Failures
- Symptoms: Squeaking noises, reduced braking efficiency, or vibration.
- Solutions: Brake pad replacement, rotor resurfacing, or brake line repairs.
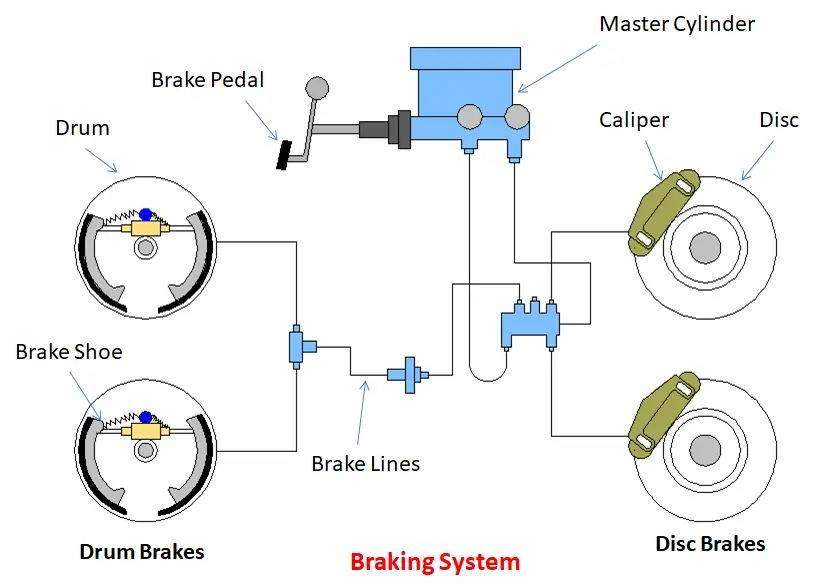
Figure: Brake System Components
4. Electrical System Issues
- Symptoms: Battery drainage, malfunctioning lights, or faulty electronics.
- Solutions: Battery replacement, alternator repairs, or electrical wiring inspections.
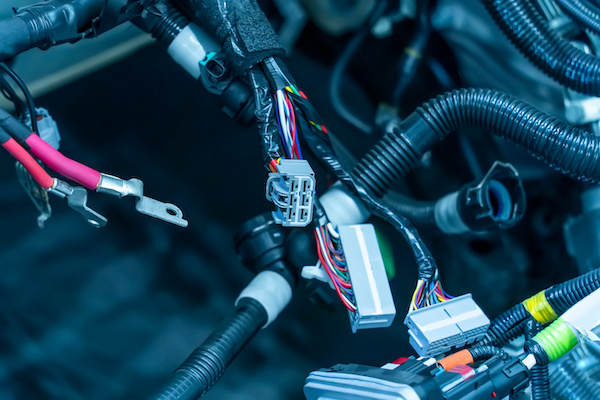
Figure: Electrical System issue
Strategies for Effective Corrective Maintenance
1. Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
- Description: Accurate diagnostics are essential for identifying the root cause of a problem. Advanced diagnostic tools and techniques can help in pinpointing issues more precisely.
- Tools: OBD-II scanners, multimeters, and diagnostic software.
2. Prioritization of Repairs
- Description: Not all faults are equally critical. Prioritizing repairs based on safety, performance, and cost implications can help manage repair schedules effectively.
- Approach: Assess the severity of the issue and its impact on vehicle operation.
3. Quality Parts and Repairs
- Description: Using high-quality replacement parts and ensuring that repairs are performed to a high standard are crucial for the longevity of the repair and vehicle reliability.
- Standards: Follow manufacturer specifications and use OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) parts where possible.
4. Record Keeping and Analysis
- Description: Maintaining detailed records of repairs and maintenance activities can provide valuable insights for future maintenance planning and help in identifying recurring issues.
- Tools: Digital maintenance logs, repair databases.
Best Practices
- Timely Intervention: Address issues as soon as they are detected to prevent further damage.
- Regular Inspections: Conduct periodic inspections to identify potential problems before they become severe.
- Skilled Technicians: Ensure that repairs are carried out by qualified technicians with the necessary expertise.
- Customer Communication: Keep vehicle owners informed about the nature of the repairs, expected costs, and timeframes.
Conclusion
Corrective maintenance plays a vital role in ensuring the reliability and safety of vehicles. By understanding the principles, strategies, and best practices associated with corrective maintenance, automotive professionals can effectively manage repairs, minimize downtime, and enhance vehicle performance. Proactive and skilled approach to corrective maintenance is essential for maintaining the longevity and efficiency of automobiles.