←
Automobile Engineering
Global Warming
Introduction:
Climate change is one of the greatest environmental and economic challenges facing humanity. Automobile air-conditioning systems because of their design have real drawbacks in terms of greenhouse gas emission.
Greenhouse effect
- As a result of the use of large quantities of fossil fuel (such as oil, coal and spontaneous gas) and the depletion of forests, the concentration of carbonic acid, Freon, methane etc. in the atmosphere is increasing.
- The heat from the surface of the earth is being absorbed into the atmosphere. Under these conditions, it is thought that the earth is getting warmer, i.e. global warming.
- If conditions remain as they are and greenhouse effect gas continues to be released into the atmosphere, it is estimated that by the year 2030 the temperature will have risen by 1.5 to 4.5°C (2.7 to 8.5°F).
- The surface of the ocean will also have risen by 0.2 metres to 1.4 metres.
- Quite simply, the atmospheric release of Freon is not only causing ozone depletion, it is also bringing about the greenhouse effect.
Greenhouse effect gas
Gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2), Freon, dinitrogen monoxide (N2O), and methane (CH4) are the substances that are having an influence on the greenhouse effect. Automobile air-conditioning systems because of their design have real drawbacks in terms of greenhouse gas emission:
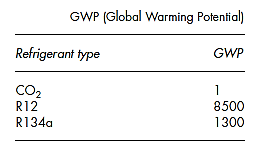
- They use refrigerants which have a high impact on the increase of the greenhouse effect. GWP (Global Warming Potential) of HFC 134a is 1300 which means that 1 kg of HFC emitted into the atmosphere has the same impact as 1.3 tons of CO2.
- Flexible hosepipes’ poor connections allow refrigerant loss.
- Compressor shaft seals are a major source of refrigerant loss.
Production, recovery, recycle, reclaim, and disposal all contribute to the greenhouse problem.