Layout Of An Automobile Chassis
Introduction of Chassis Frame
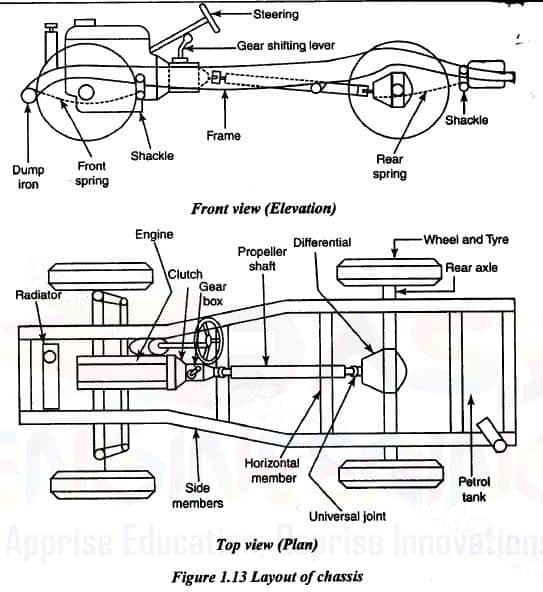
Chassis frame is the basic framework of the automobile. It supports all the parts of the automobile attached to it. It is made of drop forged steel. All the parts related to automobiles are attached to it only. All the systems related to automobile like power plant,transmission, steering, suspension, braking system etc are attached to and supported by it only
Layout Of An Automobile Chassis
“Chassis” a French term which means the complete Automobiles without Body and it includes all the systems like power plant, transmission, steering, suspension , wheels tyres , auto electric system etc. without body. If Body is also attached to it then it is known as the particular vehicle as per the shape and design of the body.
The Functions of the Chassis frame
- To carry all the stationary loads attached to it and loads of passenger and cargo carried in it.
- To withstand torsional vibration caused by the movement of the vehicle
- To withstand the centrifugal force caused by cornering of the vehicle
- To control the vibration caused by the running of the vehicle
- To withstand bending stresses due to rise and fall of the front and rear axles.
Types of Chassis frame
- Channel section
- Box section
- Tubular section
Chassis frames are the structural backbone of a vehicle, providing support for various components and ensuring the vehicle's integrity. Different types of frame sections are used to achieve specific strength and weight requirements. Here's a breakdown of the three common types:
1. Channel Section
- Shape: Resembles a letter "C" or "U" in cross-section.
- Advantages:
- Provides good resistance to bending in one direction.
- Efficient in terms of material usage.
- Easy to manufacture and fabricate.
- Applications: Commonly used in ladder-type frames, which are popular in trucks, SUVs, and heavy-duty vehicles due to their strength and versatility.
2. Box Section
- Shape: A hollow square or rectangular shape in cross-section.
- Advantages:
- Offers excellent resistance to both bending and torsion (twisting).
- Highly durable and can withstand heavy loads.
- Provides a stable platform for mounting components.
- Applications: Found in various vehicle types, including cars, trucks, and buses. Box sections are often used in unibody construction, where the frame and body are integrated into a single unit.
3. Tubular Section
- Shape: A hollow circular or oval shape in cross-section.
- Advantages:
- Offers exceptional torsional strength and rigidity.
- Lightweight compared to other sections of similar strength.
- Aesthetically pleasing, often used in sports cars and motorcycles.
- Applications: Commonly used in space frames, which are lightweight and often found in racing cars and high-performance vehicles. Tubular sections can also be used in chassis frames for various vehicle types.
Choosing the right frame section depends on factors such as the vehicle's intended use, weight capacity, and desired performance characteristics. For example, a truck might require a strong channel or box section frame to handle heavy loads, while a sports car might benefit from a lightweight tubular frame for better handling and performance.
Various loads acting on the Chassis frame
The loads acting on the chassis frame are as follow
- Stationary loads namely the loads of permanent attachment like all the parts of the chassis, body etc.
- Short duration loads while turning , braking etc.
- Momentary loads while quick acceleration , sudden braking etc.
- Loads applied while crossing roads of irregular and uneven surfaces
- Loads caused by sudden accidents, head on collisions etc.
- Loads caused by irregular and overloading of vehicles.
Different Bodies used in Automobiles
The automobiles bodies are designed according to the requirement of the vehicle. According to the design and requirement of the vehicle , there are different types of Automobiles bodies. Some of them are listed as below :
(i) Car
(ii) Straight truck
(iii) Truck with half body
(iv) Platform type truck
(v) Tractor
(vi) Tractor with articulated trailer
(vii) Tanker
(viii) Bus
(ix) Dumper truck
(x) Delivery van
(x) Station wagon
(xi) Pick up van
(xii) Jeep
(xiv) Long wheel base truck etc
Requirement of Bodies for various types of vehicle
According to requirement , automobile bodies are classified mainly into different types namely private vehicle, commercial vehicle, fleet transport vehicle, passenger transport vehicle, Ambulances vehicle used for transport of Army personnel, Ammunition etc., different types of tanker vehicle etc. If it is a private vehicle, the vehicle is used for luxury personal travelling , private cargo transport etc, namely car , mini van , Omni bus, matador etc.
If it is a commercial vehicle the vehicle is used for transportation of goods, some other vehicles, freezer boxes etc. If it is a tanker, it is used to transport milk , water, edible oils, petroleum products , gases , acids etc. The tanker bodies are designed according to the relevant requirement .
If it is an army vehicle, the vehicles are separately designed namely Arm truck, heavy long wheel base cargo trucks , long platform trucks etc. These are exclusively used to carry the army personal, arms and ammunition etc.
Some automobiles manufacturing companies are using long wheelbase trucks with closed body structure for transporting the vehicle produced in their factories to different market outlets.
The private vehicles used in different fields namely Buses of different types, air conditioned Buses, station Wagons etc, Usually Road Transport organisation of a state is a fleet organised jointly by the state Government an exclusive body which is to operate buses for travelling of passenger to various places within the state as well as Inter-State travelling also the Road transport corporation organisation is having differently designed buses namely ordinary body buses, Deluxe buses , semi luxury buses, Air conditioned buses and also buses with sleeper coach etc.
Summary: Chassis and Its Functions
Chassis is the foundational structure of an automobile. It supports all the components of the vehicle, including the engine, transmission, suspension, and body.
Key functions and considerations for chassis design:
- Structural integrity: The chassis must withstand various stresses, including:
- Centrifugal force: When cornering
- Bending stresses: Due to variations in road elevation
- Load-bearing capacity: The chassis must support the weight of the vehicle and its occupants, as well as any cargo or equipment.
- Flexibility: The chassis should be designed to absorb shocks and vibrations from the road.
Common types of chassis frames:
- Channel section: Resembles a "C" or "U" shape.
- Box section: A hollow square or rectangular shape.
- Tubular section: A hollow circular or oval shape.
Types of loads acting on a chassis:
- Stationary loads: From permanently attached components.
- Short-duration loads: During turning, braking, etc.
- Road loads: From uneven surfaces.
- Overloading: Exceeding the vehicle's weight capacity.
- Accident loads: From sudden impacts.
- Momentary loads: During quick acceleration or sudden braking.
By understanding these factors, engineers can design chassis frames that are both strong and efficient, ensuring the safety and performance of the vehicle.