←
Automobile Engineering
Power Brakes
Introduction:
Power brake is the brake that magnifies a small force applied to the brake pedal into a proportionately larger force applied to slow or stop the vehicle. Most all modern vehicles use power assisted brakes. A vacuum line from the intake manifold to the brake booster provides a source of vacuum. A brake booster check valve prevents loss of vacuum during wide open throttle.
Power brake system
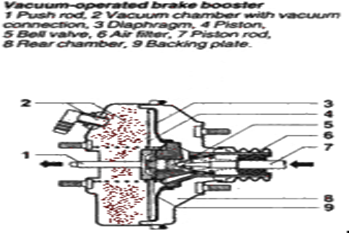
- Vacuum in the intake manifold is applied to a rubber diaphragm on the vacuum side of the booster chamber (red speckled area)
- The piston rod (7) is pushed in when the brakes are applied and vacuum is supply to the brake booster assembly rear section through the bell valve.
- When the engine is running and the brake are not depressed there is vacuum on both sides the booster diaphragm (vacuum Suspended)
- As brakes are applied atmospheric pressure is allowed to enter the rear of the booster through an air control valve increasing pressure on the master cylinder.
Working:
- When the brake pedal is depressed the air valve moves forward allowing atmospheric pressure to enter the rear of the brake booster assembly.
- The higher pressure in the rear forces the diaphragm to move forward increasing the pressure applied to the master cylinder.
- A spring in the front chamber forces the diaphragm rearward when the brake pedal is released.
- Most automotive repair shop does not repair or rebuild brake boosters. It is usually more cost efficient to replace defective brake booster assemblies.
- It is important to understand how a power brake booster operates before diagnosing a defective booster assembly.
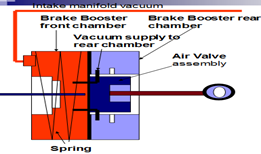
To diagnose a power brake assembly
- Pump the brake several times with the engine off to remove vacuum from the booster.
- Start the vehicle the brake pedal should move downward slowly as vacuum begins to build.
- A hard brake pedal can be caused by:
A. Defective brake booster diaphragm
B. Low vacuum to the brake booster.
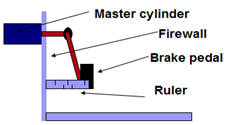
- There are very few adjustments on power assisted brakes. If necessary brake pedals free travel can be checked using a ruler.
- If a push rod is adjusted to short it will cause excesses brake pedal free travel
- If a push rod is adjusted to long it could cause brake to:
Heat up due to dragging
Lock-up due to brake expanding caused by excesses heat.