←
Automobile Engineering
Shock Absorber Design
Introduction:
Two front shock absorbers are connected from the front suspension to the chassis, and two rear shock absorbers are attached between the rear suspension and the chassis.
Purpose of the shock absorber:
Shock absorbers have three main purposes:
1. They control spring action and oscillations to provide the desired ride quality.
2. They help prevent body sway and lean while cornering.
3. They reduce the tendency of a tire tread to lift off the road, which improves tire life, traction, and directional stability.
Shock absorber design is matched to the deflection rate of the coil spring to control the spring action. Several different types of shock absorbers are available for special service requirements.
Shock Absorber Design
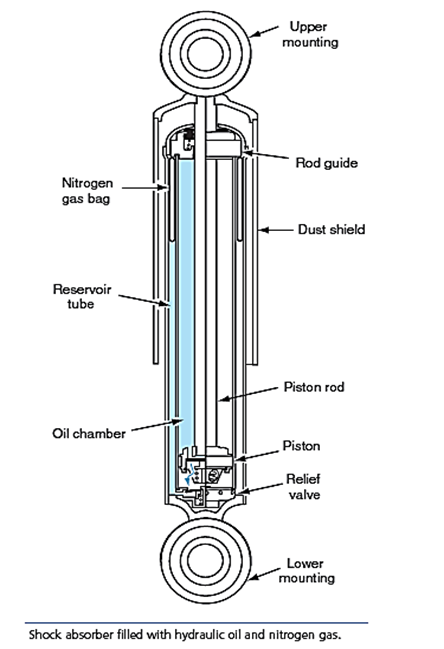
- The lower half of a shock absorber is a twin tube steel unit filled with hydraulic oil and nitrogen gas.
- In some shock absorbers, the nitrogen gas is omitted.
- A relief valve is located in the bottom of the unit, and a circular lower mounting is attached to the lower tube.
- This mounting contains a rubber isolating bushing, or grommet.
- A piston and rod assembly is connected to the upper half of the shock absorber.
- This upper portion of the shock absorber has a dust shield that surrounds the lower twin tube unit.
- The piston is precision fit in the inner cylinder of the lower unit.
- A piston rod guide and seal are located in the top of the lower unit.\
- A circular upper mounting with a rubber bushing is attached to the top of the shock absorber