←
Automobile Engineering
The Basic Theory Of Cooling
Introduction:
Modern automotive internal combustion engines generate a huge amount of heat. This heat is created when the gasoline and air mixture is ignited in the combustion chamber. This explosion causes the piston to be forced down inside the engine, levering the connecting rods, and turning the crankshaft, creating power. Metal temperatures around the combustion chamber can exceed1000° F. In order to prevent the overheating of the engine oil, cylinder walls, pistons, valves, and other components by these extreme temperatures, it is necessary to effectively dispose of the heat.
Selection of the cooling system:
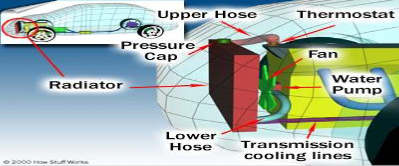
- Modern automotive engines have basically dumped the Air Cooled System for the more effective Liquid Cooled System to handle the job.
- In a liquid cooled system, heat is carried away by the use of a heat absorbing coolant that circulates through the engine, especially around the combustion chamber in the cylinder head area of the engine block.
- The coolant is pumped through the engine, then after absorbing the heat of combustion is circulated to the radiator where the heat is transferred to the atmosphere.
- The cooled liquid is then transferred back into the engine to repeat the process. Excessive cooling system capacity can also be harmful, and may affect engine life and performance.
- Coolant temperatures also affect oil temperatures and more engine wear occurs when the engine oil is below 190° F.
- An effective cooling system controls the engine temperature within a specific range so that the engine stays within peak performance.
Cooling System Functions:
- Temperatures in the combustion chamber of the engine can reach 4,500 F (2,500 C) [2], so cooling the area around the cylinders is critical.
- Areas around the exhaust valves are especially for structure is filled with coolant. If the engine goes without cooling, the metal got hot enough for the piston to weld itself to the cylinder.
- This usually means the complete destruction of the engine. The cooling system removes enough heat to keep the engine at a safe temperature for best performance.
- A secondary function of the cooling system is to provide interior cabin heat during cold winter.