Generator Types & Characteristics
Generator types & its Characteristics: D.C generators may be classified as (i) separately excited generator, (ii) shunt generator, and (iii) series generator and (iv) compound generator.
In a separately excited generator field winding is energised from a separate voltage source in order to produce flux in the machine. So long the machine operates in unsaturated condition the flux produced will be proportional to the field current. In order to implement shunt connection, the field winding is connected in parallel with the armature. It will be shown that subject to fulfillment of certain conditions, the machine may have sufficient field current developed on its own by virtue of its shunt connection.
In series d.c machine, there is one field winding wound over the main poles with fewer turns and large cross sectional area. Series winding is meant to be connected in series with the armature and naturally to be designed for rated armature current. Obviously there will be practically no voltage or very small voltage due to residual field under no load condition (Ia = 0). However, field gets strengthened as load will develop rated voltage across the armature with reverse polarity, is connected and terminal voltage increases. Variation in load resistance causes the terminal voltage to vary. Terminal voltage will start falling, when saturation sets in and armature reaction effect becomes pronounced at large load current. Hence, series generators are not used for delivering power at constant voltage. Series generator found application in boosting up voltage in d.c transmission system.
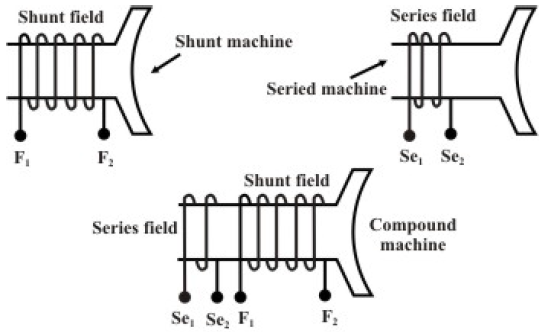
A compound generator has two separate field coils wound over the field poles. The coil having large number of turns and thinner cross sectional area is called the shunt field coil and the other coil having few number of turns and large cross sectional area is called the series field coil. Series coil is generally connected in series with the armature while the shunt field coil is connected in parallel with the armature. If series coil is left alone without any connection, then it becomes a shunt machine with the other coil connected in parallel. Placement of field coils for shunt, series and compound generators are shown in figure 38.1. Will develop rated voltage across the armature with reverse polarity.