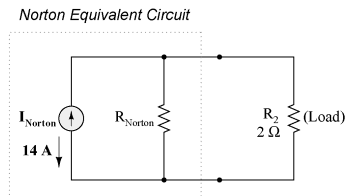
Norton's Theorem
Norton's Theorem: Norton's Theorem states that it is possible to simplify any linear circuit, no matter how complex, to an equivalent circuit with just a single current source and parallel resistance connected to a load. Just as with Thevenin's Theorem, the qualification of "linear" is identical to that found in the Superposition Theorem: all underlying equations must be linear (no exponents or roots).
Contrasting our original example circuit against the Norton equivalent: it looks something like this:
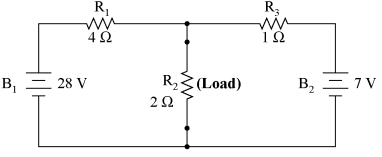
. . . after Norton conversion . . .
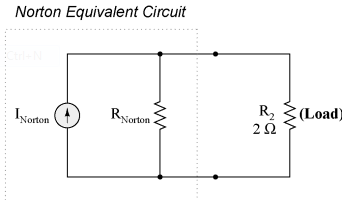
Remember that a current source is a component whose job is to provide a constant amount of current, outputting as much or as little voltage necessary to maintain that constant current. As with Thevenin's Theorem, everything in the original circuit except the load resistance has been reduced to an equivalent circuit that is simpler to analyze. Also similar to Thevenin's Theorem are the steps used in Norton's Theorem to calculate the Norton source current (INorton) and Norton resistance (RNorton). As before, the first step is to identify the load resistance and remove it from the original circuit:
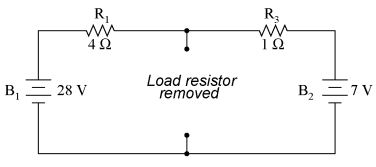
Then, to find the Norton current (for the current source in the Norton equivalent circuit), place a direct wire (short) connection between the load points and determine the resultant current. Note that this step is exactly opposite the respective step in Thevenin's Theorem, where we replaced the load resistor with a break (open circuit):
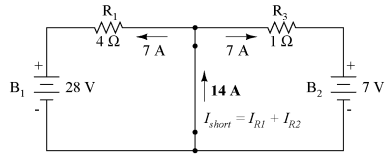
With zero voltage dropped between the load resistor connection points, the current through R1 is strictly a function of B1's voltage and R1's resistance: 7 amps (I=E/R). Likewise, the current through R3 is now strictly a function of B2's voltage and R3's resistance: 7 amps (I=E/R). The total current through the short between the load connection points is the sum of these two currents: 7 amps 7 amps = 14 amps. This figure of 14 amps becomes the Norton source current (INorton) in our equivalent circuit: