Three-phase Y And Delta Configurations
Three-phase Y and Delta configurations: Initially we explored the idea of three-phase power systems by connecting three voltage sources together in what is commonly known as the “Y” (or “star”) configuration. This configuration of voltage sources is characterized by a common connection point joining one side of each source. (Figure below)
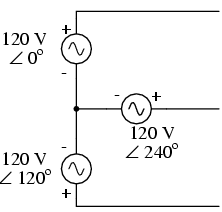
Three-phase “Y” connection has three voltage sources connected to a common point.
If we draw a circuit showing each voltage source to be a coil of wire (alternator or transformer winding) and do some slight rearranging, the “Y” configuration becomes more obvious in Figure below.
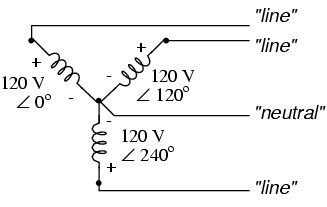 Three-phase, four-wire “Y” connection uses a "common" fourth wire.
Three-phase, four-wire “Y” connection uses a "common" fourth wire.
If we draw a circuit showing each voltage source to be a coil of wire (alternator or transformer winding) and do some slight rearranging, the “Y” configuration becomes more obvious in Figure below.
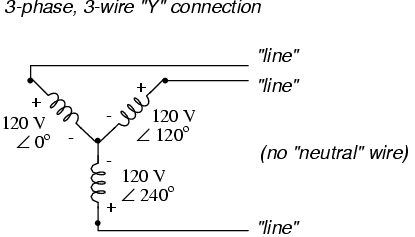 Three-phase, three-wire “Y” connection does not use the neutral wire.
Three-phase, three-wire “Y” connection does not use the neutral wire.
When we measure voltage and current in three-phase systems, we need to be specific as to where we're measuring. Line voltage refers to the amount of voltage measured between any two line conductors in a balanced three-phase system. With the above circuit, the line voltage is roughly 208 volts. Phase voltage refers to the voltage measured across any one component (source winding or load impedance) in a balanced three-phase source or load. For the circuit shown above, the phase voltage is 120 volts. The terms line current and phase current follow the same logic: the former referring to current through any one line conductor, and the latter to current through any one component.
Y-connected sources and loads always have line voltages greater than phase voltages, and line currents equal to phase currents. If the Y-connected source or load is balanced, the line voltage will be equal to the phase voltage times the square root of 3:
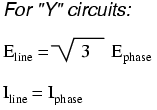
However, the “Y” configuration is not the only valid one for connecting three-phase voltage source or load elements together. Another configuration is known as the “Delta,” for its geometric resemblance to the Greek letter of the same name (Δ). Take close notice of the polarity for each winding in Figure below.
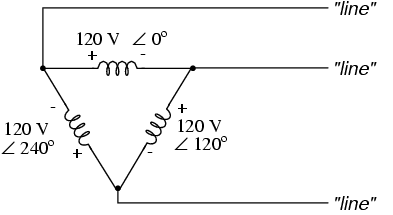 Three-phase, three-wire Δ connection has no common.
Three-phase, three-wire Δ connection has no common.