Closed Loop Systems
Closed loop systems:
Fig 1: Process to be controlled
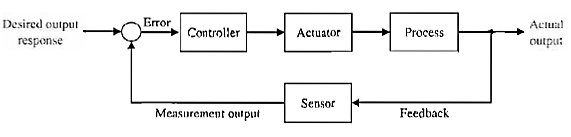
Fig: 2 Closed loop control system
Feedback control systems:
A system that maintains a prescribed relationship between the output and the reference input by comparing them and using the difference as a means of control is called a feedback control system. An example would be a room-temperature control system. By measuring the actual room temperature and comparing it with the reference temperature (desired temperature), the thermostat turns the heating or cooling equipment on or off in such a way as to ensure that the room temperature remains at a comfortable level regardless of outside conditions.
Feedback control systems are not limited to engineering but can be found in various non-engineering fields as well. The human body, for instance, is a highly advanced feedback control system. Both body temperature and blood pressure are kept constant by means of physiological feedback. In fact, feedback performs a vital function: It makes the human body relatively insensitive to external disturbances, thus enabling it to function properly in a changing environment.
Closed-loop control systems
In contrast to an open-loop control system, a closed-loop control system utilizes an additional measure of the actual output to compare the actual output with the desired output response. The measure of the output is called the feedback signal. A simple closed-loop feedback control .system is shown in Figure 2. A feedback control system is a control system that tends to maintain a prescribed relationship of one system variable to another by comparing functions of these variables and using the difference as a means of control. With an accurate sensor, the measured output is a good approximation of the actual output of the system.
Feedback control systems are often referred to as closed-loop control systems. In practice, the terms feedback control and closed-loop control are used interchangeably. In a closed-loop control system the actuating error signal, which is the difference between the input signal and the feedback signal (which may be the output signal itself or a function of the output signal and its derivatives and/or integrals), is fed to the controller so as to reduce the error and bring the output of the system to a desired value. The term closed-loop control always implies the use of feedback control action in order to reduce system error.