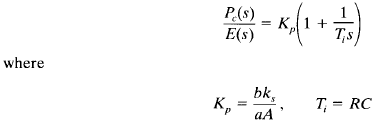Pi Controllers
PI controllers
Due to the restriction of the valve in the path to bellows II, there will be a pressure drop across the valve. As time goes on, air will flow across the valve in such a way that the change in pressure in bellows II attains the value pc. Thus bellows II will expand or contract as time elapses in such a way as to move the flapper an additional amount in the direction of the original displacement e. This will cause the back pressure pc in the nozzle to change continuously, as shown in Figure 2(b).
Note that the integral control action in the controller takes the form of slowly canceling the feedback that the proportional control originally provided.
A block diagram of this controller under the assumption of small variations in the variables is shown in Figure 2(c). A simplification of this block diagram yields Figure 2(d). The transfer function of this controller is
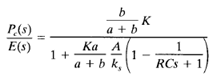
where K is a constant, A is the area of the bellows, and ks is the equivalent spring constant of the combined bellows. If 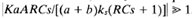 , which is usually the case, the transfer function can be simplified to
, which is usually the case, the transfer function can be simplified to