
“Where do they get matter to fill up a page in this little island lost in the wastes of the Indian Ocean? Oh, Madagascar. They discuss Madagascar and France. That is the bulk. Then they chock up the rest with advice to the Government. Also, slurs upon the English administration. The papers are all owned and edited by creoles—French.
“The language of the country is French. Everybody speaks it—has to. You have to know French particularly mongrel French, the patois spoken by Tom, Dick, and Harry of the multiform complexions—or you can’t get along.
“This was a flourishing country in former days, for it made then and still makes the best sugar in the world; but first the Suez Canal severed it from the world and left it out in the cold and next the beetroot sugar helped by bounties, captured the European markets. Sugar is the life of Mauritius, and it is losing its grip. Its downward course was checked by the depreciation of the rupee—for the planter pays wages in rupees but sells his crop for gold—and the insurrection in Cuba and paralyzation of the sugar industry there have given our prices here a life-saving lift; but the outlook has nothing permanently favorable about it. It takes a year to mature the canes—on the high ground three and six months longer—and there is always a chance that the annual cyclone will rip the profit out of the crop. In recent times a cyclone took the whole crop, as you may say; and the island never saw a finer one. Some of the noblest sugar estates in the island are in deep difficulties. A dozen of them are investments of English capital; and the companies that own them are at work now, trying to settle up and get out with a saving of half the money they put in. You know, in these days, when a country begins to introduce the tea culture, it means that its own specialty has gone back on it. Look at Bengal; look at Ceylon. Well, they’ve begun to introduce the tea culture, here.
“Many copies of Paul and Virginia are sold every year in Mauritius. No
other book is so popular here except the Bible. By many it is supposed to
be a part of the Bible. All the missionaries work up their French on it
when they come here to pervert the Catholic mongrel. It is the greatest
story that was ever written about Mauritius, and the only one."
CHAPTER LXIII.
The principal difference between a cat and a lie is that the cat has only nine lives.
—Pudd’nhead Wilson’s New Calendar.
April 20.—The cyclone of 1892 killed and crippled hundreds of people; it was accompanied by a deluge of rain, which drowned Port Louis and produced a water famine. Quite true; for it burst the reservoir and the water-pipes; and for a time after the flood had disappeared there was much distress from want of water.
This is the only place in the world where no breed of matches can stand
the damp. Only one match in 16 will light.

The roads are hard and smooth; some of the compounds are spacious, some of the bungalows commodious, and the roadways are walled by tall bamboo hedges, trim and green and beautiful; and there are azalea hedges, too, both the white and the red; I never saw that before.
As to healthiness: I translate from to-day’s (April 20) Merchants’ and Planters’ Gazette, from the article of a regular contributor, “Carminge,” concerning the death of the nephew of a prominent citizen:
“Sad and lugubrious existence, this which we lead in Mauritius; I believe there is no other country in the world where one dies more easily than among us. The least indisposition becomes a mortal malady; a simple headache develops into meningitis; a cold into pneumonia, and presently, when we are least expecting it, death is a guest in our home.”
This daily paper has a meteorological report which tells you what the weather was day before yesterday.
One is never pestered by a beggar or a peddler in this town, so far as I can see. This is pleasantly different from India.
April 22. To such as believe that the quaint product called French civilization would be an improvement upon the civilization of New Guinea and the like, the snatching of Madagascar and the laying on of French civilization there will be fully justified. But why did the English allow the French to have Madagascar? Did she respect a theft of a couple of centuries ago? Dear me, robbery by European nations of each other’s territories has never been a sin, is not a sin to-day. To the several cabinets the several political establishments of the world are clotheslines; and a large part of the official duty of these cabinets is to keep an eye on each other’s wash and grab what they can of it as opportunity offers. All the territorial possessions of all the political establishments in the earth—including America, of course—consist of pilferings from other people’s wash. No tribe, howsoever insignificant, and no nation, howsoever mighty, occupies a foot of land that was not stolen. When the English, the French, and the Spaniards reached America, the Indian tribes had been raiding each other’s territorial clothes-lines for ages, and every acre of ground in the continent had been stolen and re-stolen 500 times. The English, the French, and the Spaniards went to work and stole it all over again; and when that was satisfactorily accomplished they went diligently to work and stole it from each other. In Europe and Asia and Africa every acre of ground has been stolen several millions of times. A crime persevered in a thousand centuries ceases to be a crime, and becomes a virtue. This is the law of custom, and custom supersedes all other forms of law. Christian governments are as frank to-day, as open and above-board, in discussing projects for raiding each other’s clothes-lines as ever they were before the Golden Rule came smiling into this inhospitable world and couldn’t get a night’s lodging anywhere. In 150 years England has beneficently retired garment after garment from the Indian lines, until there is hardly a rag of the original wash left dangling anywhere. In 800 years an obscure tribe of Muscovite savages has risen to the dazzling position of Land-Robber-in-Chief; she found a quarter of the world hanging out to dry on a hundred parallels of latitude, and she scooped in the whole wash. She keeps a sharp eye on a multitude of little lines that stretch along the northern boundaries of India, and every now and then she snatches a hip-rag or a pair of pyjamas. It is England’s prospective property, and Russia knows it; but Russia cares nothing for that. In fact, in our day land-robbery, claim-jumping, is become a European governmental frenzy. Some have been hard at it in the borders of China, in Burma, in Siam, and the islands of the sea; and all have been at it in Africa. Africa has been as coolly divided up and portioned out among the gang as if they had bought it and paid for it. And now straightway they are beginning the old game again—to steal each other’s grabbings. Germany found a vast slice of Central Africa with the English flag and the English missionary and the English trader scattered all over it, but with certain formalities neglected—no signs up, “Keep off the grass,” “Trespassers-forbidden,” etc.—and she stepped in with a cold calm smile and put up the signs herself, and swept those English pioneers promptly out of the country.
There is a tremendous point there. It can be put into the form of a maxim: Get your formalities right—never mind about the moralities.
It was an impudent thing; but England had to put up with it. Now, in the case of Madagascar, the formalities had originally been observed, but by neglect they had fallen into desuetude ages ago. England should have snatched Madagascar from the French clothes-line. Without an effort she could have saved those harmless natives from the calamity of French civilization, and she did not do it. Now it is too late.
The signs of the times show plainly enough what is going to happen. All the savage lands in the world are going to be brought under subjection to the Christian governments of Europe. I am not sorry, but glad. This coming fate might have been a calamity to those savage peoples two hundred years ago; but now it will in some cases be a benefaction. The sooner the seizure is consummated, the better for the savages.
The dreary and dragging ages of bloodshed and disorder and oppression will give place to peace and order and the reign of law. When one considers what India was under her Hindoo and Mohammedan rulers, and what she is now; when he remembers the miseries of her millions then and the protections and humanities which they enjoy now, he must concede that the most fortunate thing that has ever befallen that empire was the establishment of British supremacy there. The savage lands of the world are to pass to alien possession, their peoples to the mercies of alien rulers. Let us hope and believe that they will all benefit by the change.
April 23. “The first year they gather shells; the second year they gather
shells and drink; the third year they do not gather shells.” (Said of
immigrants to Mauritius.)

Population 375,000. 120 sugar factories.
Population 1851, 185,000. The increase is due mainly to the introduction of Indian coolies. They now apparently form the great majority of the population. They are admirable breeders; their homes are always hazy with children. Great savers of money. A British officer told me that in India he paid his servant 10 rupees a month, and he had 11 cousins, uncles, parents, etc., dependent upon him, and he supported them on his wages. These thrifty coolies are said to be acquiring land a trifle at a time, and cultivating it; and may own the island by and by.
The Indian women do very hard labor (for wages running from 40 one
hundredths of a rupee for twelve hours’ work to 50 one hundredths of a
rupee.) They carry mats of sugar on their heads (70 pounds) all day lading
ships, for half a rupee, and work at gardening all day for less.

The camaron is a fresh water creature like a cray-fish. It is regarded here as the world’s chiefest delicacy—and certainly it is good. Guards patrol the streams to prevent poaching it. A fine of Rs.200 or 300 (they say) for poaching. Bait is thrown in the water; the camaron goes for it; the fisher drops his loop in and works it around and about the camaron he has selected, till he gets it over its tail; then there’s a jerk or something to certify the camaron that it is his turn now; he suddenly backs away, which moves the loop still further up his person and draws it taut, and his days are ended.
Another dish, called palmiste, is like raw turnip-shavings and tastes like green almonds; is very delicate and good. Costs the life of a palm tree 12 to 20 years old—for it is the pith.
Another dish—looks like greens or a tangle of fine seaweed—is a preparation of the deadly nightshade. Good enough.
The monkeys live in the dense forests on the flanks of the toy mountains, and they flock down nights and raid the sugar-fields. Also on other estates they come down and destroy a sort of bean-crop—just for fun, apparently—tear off the pods and throw them down.
The cyclone of 1892 tore down two great blocks of stone buildings in the
center of Port Louis—the chief architectural feature—and left
the uncomely and apparently frail blocks standing. Everywhere in its track
it annihilated houses, tore off roofs, destroyed trees and crops. The men
were in the towns, the women and children at home in the country getting
crippled, killed, frightened to insanity; and the rain deluging them, the
wind howling, the thunder crashing, the lightning glaring. This for an
hour or so. Then a lull and sunshine; many ventured out of safe shelter;
then suddenly here it came again from the opposite point and renewed and
completed the devastation. It is said the Chinese fed the sufferers for
days on free rice.
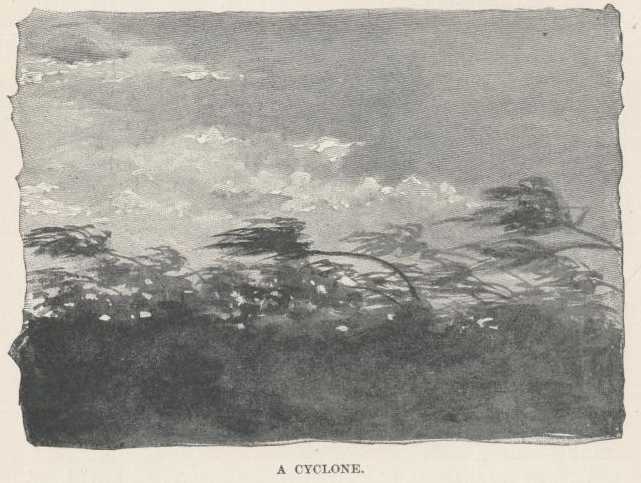

Whole streets in Port Louis were laid flat—wrecked. During a minute and a half the wind blew 123 miles an hour; no official record made after that, when it may have reached 150. It cut down an obelisk. It carried an American ship into the woods after breaking the chains of two anchors. They now use four-two forward, two astern. Common report says it killed 1,200 in Port Louis alone, in half an hour. Then came the lull of the central calm—people did not know the barometer was still going down—then suddenly all perdition broke loose again while people were rushing around seeking friends and rescuing the wounded. The noise was comparable to nothing; there is nothing resembling it but thunder and cannon, and these are feeble in comparison.
What there is of Mauritius is beautiful. You have undulating wide expanses of sugar-cane—a fine, fresh green and very pleasant to the eye; and everywhere else you have a ragged luxuriance of tropic vegetation of vivid greens of varying shades, a wild tangle of underbrush, with graceful tall palms lifting their crippled plumes high above it; and you have stretches of shady dense forest with limpid streams frolicking through them, continually glimpsed and lost and glimpsed again in the pleasantest hide-and-seek fashion; and you have some tiny mountains, some quaint and picturesque groups of toy peaks, and a dainty little vest-pocket Matterhorn; and here and there and now and then a strip of sea with a white ruffle of surf breaks into the view.
That is Mauritius; and pretty enough. The details are few, the massed result is charming, but not imposing; not riotous, not exciting; it is a Sunday landscape. Perspective, and the enchantments wrought by distance, are wanting. There are no distances; there is no perspective, so to speak. Fifteen miles as the crow flies is the usual limit of vision. Mauritius is a garden and a park combined. It affects one’s emotions as parks and gardens affect them. The surfaces of one’s spiritual deeps are pleasantly played upon, the deeps themselves are not reached, not stirred. Spaciousness, remote altitudes, the sense of mystery which haunts apparently inaccessible mountain domes and summits reposing in the sky—these are the things which exalt the spirit and move it to see visions and dream dreams.
The Sandwich Islands remain my ideal of the perfect thing in the matter of
tropical islands. I would add another story to Mauna Loa’s 16,000 feet if
I could, and make it particularly bold and steep and craggy and forbidding
and snowy; and I would make the volcano spout its lava-floods out of its
summit instead of its sides; but aside from these non-essentials I have no
corrections to suggest. I hope these will be attended to; I do not wish to
have to speak of it again.
CHAPTER LXIV.
When your watch gets out of order you have choice of two things to do: throw it in the fire or take it to the watch-tinker. The former is the quickest.
—Pudd’nhead Wilson’s New Calendar.
The Arundel Castle is the finest boat I have seen in these seas. She is thoroughly modern, and that statement covers a great deal of ground. She has the usual defect, the common defect, the universal defect, the defect that has never been missing from any ship that ever sailed—she has imperfect beds. Many ships have good beds, but no ship has very good ones. In the matter of beds all ships have been badly edited, ignorantly edited, from the beginning. The selection of the beds is given to some hearty, strong-backed, self-made man, when it ought to be given to a frail woman accustomed from girlhood to backaches and insomnia. Nothing is so rare, on either side of the ocean, as a perfect bed; nothing is so difficult to make. Some of the hotels on both sides provide it, but no ship ever does or ever did. In Noah’s Ark the beds were simply scandalous. Noah set the fashion, and it will endure in one degree of modification or another till the next flood.
8 A.M. Passing Isle de Bourbon. Broken-up sky-line of volcanic mountains in the middle. Surely it would not cost much to repair them, and it seems inexcusable neglect to leave them as they are.
It seems stupid to send tired men to Europe to rest. It is no proper rest
for the mind to clatter from town to town in the dust and cinders, and
examine galleries and architecture, and be always meeting people and
lunching and teaing and dining, and receiving worrying cables and letters.
And a sea voyage on the Atlantic is of no use—voyage too short, sea
too rough. The peaceful Indian and Pacific Oceans and the long stretches
of time are the healing thing.

May 2, AM. A fair, great ship in sight, almost the first we have seen in these weeks of lonely voyaging. We are now in the Mozambique Channel, between Madagascar and South Africa, sailing straight west for Delagoa Bay.
Last night, the burly chief engineer, middle-aged, was standing telling a spirited seafaring tale, and had reached the most exciting place, where a man overboard was washing swiftly astern on the great seas, and uplifting despairing cries, everybody racing aft in a frenzy of excitement and fading hope, when the band, which had been silent a moment, began impressively its closing piece, the English national anthem. As simply as if he was unconscious of what he was doing, he stopped his story, uncovered, laid his laced cap against his breast, and slightly bent his grizzled head. The few bars finished, he put on his cap and took up his tale again, as naturally as if that interjection of music had been a part of it. There was something touching and fine about it, and it was moving to reflect that he was one of a myriad, scattered over every part of the globe, who by turn was doing as he was doing every hour of the twenty-four—those awake doing it while the others slept—those impressive bars forever floating up out of the various climes, never silent and never lacking reverent listeners.
All that I remember about Madagascar is that Thackeray’s little Billie went up to the top of the mast and there knelt him upon his knee, saying, “I see
|
“Jerusalem and Madagascar, And North and South Amerikee." |
May 3. Sunday. Fifteen or twenty Africanders who will end their voyage
to-day and strike for their several homes from Delagoa Bay to-morrow, sat
up singing on the afterdeck in the moonlight till 3 A.M. Good fun and
wholesome. And the songs were clean songs, and some of them were hallowed
by tender associations.
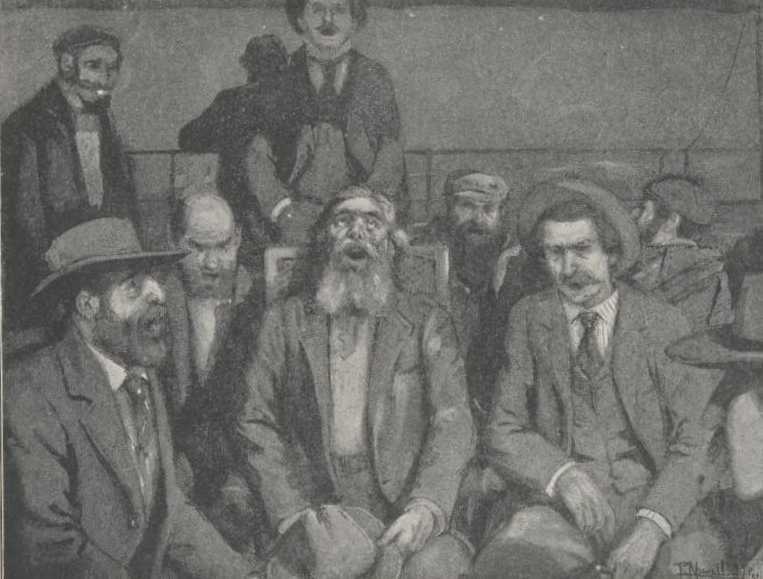

Finally, in a pause, a man asked, “Have you heard about the fellow that kept a diary crossing the Atlantic?” It was a discord, a wet blanket. The men were not in the mood for humorous dirt. The songs had carried them to their homes, and in spirit they sat by those far hearthstones, and saw faces and heard voices other than those that were about them. And so this disposition to drag in an old indecent anecdote got no welcome; nobody answered. The poor man hadn’t wit enough to see that he had blundered, but asked his question again. Again there was no response. It was embarrassing for him. In his confusion he chose the wrong course, did the wrong thing—began the anecdote. Began it in a deep and hostile stillness, where had been such life and stir and warm comradeship before. He delivered himself of the brief details of the diary’s first day, and did it with some confidence and a fair degree of eagerness. It fell flat. There was an awkward pause. The two rows of men sat like statues. There was no movement, no sound. He had to go on; there was no other way, at least none that an animal of his calibre could think of. At the close of each day’s diary, the same dismal silence followed. When at last he finished his tale and sprung the indelicate surprise which is wont to fetch a crash of laughter, not a ripple of sound resulted. It was as if the tale had been told to dead men. After what seemed a long, long time, somebody sighed, somebody else stirred in his seat; presently, the men dropped into a low murmur of confidential talk, each with his neighbor, and the incident was closed. There were indications that that man was fond of his anecdote; that it was his pet, his standby, his shot that never missed, his reputation-maker. But he will never tell it again. No doubt he will think of it sometimes, for that cannot well be helped; and then he will see a picture, and always the same picture—the double rank of dead men; the vacant deck stretching away in dimming perspective beyond them, the wide desert of smooth sea all abroad; the rim of the moon spying from behind a rag of black cloud; the remote top of the mizzenmast shearing a zigzag path through the fields of stars in the deeps of space; and this soft picture will remind him of the time that he sat in the midst of it and told his poor little tale and felt so lonesome when he got through.
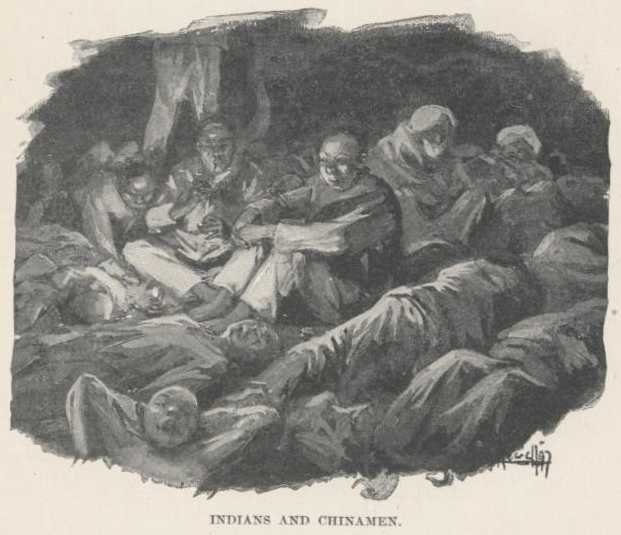
Fifty Indians and Chinamen asleep in a big tent in the waist of the ship
forward; they lie side by side with no space between; the former wrapped
up, head and all, as in the Indian streets, the Chinamen uncovered; the
lamp and things for opium smoking in the center.
A passenger said it was ten 2-ton truck loads of dynamite that lately exploded at Johannesburg. Hundreds killed; he doesn’t know how many; limbs picked up for miles around. Glass shattered, and roofs swept away or collapsed 200 yards off; fragment of iron flung three and a half miles.
It occurred at 3 p.m.; at 6, L65,000 had been subscribed. When this passenger left, L35,000 had been voted by city and state governments and L100,000 by citizens and business corporations. When news of the disaster was telephoned to the Exchange L35,000 were subscribed in the first five minutes. Subscribing was still going on when he left; the papers had ceased the names, only the amounts—too many names; not enough room. L100,000 subscribed by companies and citizens; if this is true, it must be what they call in Australia “a record”—the biggest instance of a spontaneous outpour for charity in history, considering the size of the population it was drawn from, $8 or $10 for each white resident, babies at the breast included.
Monday, May 4. Steaming slowly in the stupendous Delagoa Bay, its dim arms stretching far away and disappearing on both sides. It could furnish plenty of room for all the ships in the world, but it is shoal. The lead has given us 3 1/2 fathoms several times and we are drawing that, lacking 6 inches.
A bold headland—precipitous wall, 150 feet high, very strong, red color, stretching a mile or so. A man said it was Portuguese blood—battle fought here with the natives last year. I think this doubtful. Pretty cluster of houses on the tableland above the red and rolling stretches of grass and groups of trees, like England.
The Portuguese have the railroad (one passenger train a day) to the border—70 miles—then the Netherlands Company have it. Thousands of tons of freight on the shore—no cover. This is Portuguese allover—indolence, piousness, poverty, impotence.
Crews of small boats and tugs, all jet black woolly heads and very muscular.
Winter. The South African winter is just beginning now, but nobody but an expert can tell it from summer. However, I am tired of summer; we have had it unbroken for eleven months. We spent the afternoon on shore, Delagoa Bay. A small town—no sights. No carriages. Three ‘rickshas, but we couldn’t get them—apparently private. These Portuguese are a rich brown, like some of the Indians. Some of the blacks have the long horse heads and very long chins of the negroes of the picture books; but most of them are exactly like the negroes of our Southern States round faces, flat noses, good-natured, and easy laughers.
Flocks of black women passed along, carrying outrageously heavy bags of freight on their heads. The quiver of their leg as the foot was planted and the strain exhibited by their bodies showed what a tax upon their strength the load was. They were stevedores and doing full stevedore’s work. They were very erect when unladden—from carrying heavy loads on their heads—just like the Indian women. It gives them a proud fine carriage.
Sometimes one saw a woman carrying on her head a laden and top-heavy
basket the shape of an inverted pyramid—its top the size of a
soup-plate, its base the diameter of a teacup. It required nice balancing—and
got it.

No bright colors; yet there were a good many Hindoos.
The Second Class Passenger came over as usual at “lights out” (11) and we lounged along the spacious vague solitudes of the deck and smoked the peaceful pipe and talked. He told me an incident in Mr. Barnum’s life which was evidently characteristic of that great showman in several ways:
This was Barnum’s purchase of Shakespeare’s birthplace, a quarter of a century ago. The Second Class Passenger was in Jamrach’s employ at the time and knew Barnum well. He said the thing began in this way. One morning Barnum and Jamrach were in Jamrach’s little private snuggery back of the wilderness of caged monkeys and snakes and other commonplaces of Jamrach’s stock in trade, refreshing themselves after an arduous stroke of business, Jamrach with something orthodox, Barnum with something heterodox—for Barnum was a teetotaler. The stroke of business was in the elephant line. Jamrach had contracted to deliver to Barnum in New York 18 elephants for $360,000 in time for the next season’s opening. Then it occurred to Mr. Barnum that he needed a “card”. He suggested Jumbo. Jamrach said he would have to think of something else—Jumbo couldn’t be had; the Zoo wouldn’t part with that elephant. Barnum said he was willing to pay a fortune for Jumbo if he could get him. Jamrach said it was no use to think about it; that Jumbo was as popular as the Prince of Wales and the Zoo wouldn’t dare to sell him; all England would be outraged at the idea; Jumbo was an English institution; he was part of the national glory; one might as well think of buying the Nelson monument. Barnum spoke up with vivacity and said:
“It’s a first-rate idea. I’ll buy the Monument.”
Jamrach was speechless for a second. Then he said, like one ashamed “You caught me. I was napping. For a moment I thought you were in earnest.”
Barnum said pleasantly—
“I was in earnest. I know they won’t sell it, but no matter, I will not throw away a good idea for all that. All I want is a big advertisement. I will keep the thing in mind, and if nothing better turns up I will offer to buy it. That will answer every purpose. It will furnish me a couple of columns of gratis advertising in every English and American paper for a couple of months, and give my show the biggest boom a show ever had in this world.”
Jamrach started to deliver a burst of admiration, but was interrupted by Barnum, who said:
“Here is a state of things! England ought to blush.”
His eye had fallen upon something in the newspaper. He read it through to himself, then read it aloud. It said that the house that Shakespeare was born in at Stratford-on-Avon was falling gradually to ruin through neglect; that the room where the poet first saw the light was now serving as a butcher’s shop; that all appeals to England to contribute money (the requisite sum stated) to buy and repair the house and place it in the care of salaried and trustworthy keepers had fallen resultless. Then Barnum said:
“There’s my chance. Let Jumbo and the Monument alone for the present—they’ll
keep. I’ll buy Shakespeare’s house. I’ll set it up in my Museum in New
York and put a glass case around it and make a sacred thing of it; and
you’ll see all America flock there to worship; yes, and pilgrims from the
whole earth; and I’ll make them take their hats off, too. In America we
know how to value anything that Shakespeare’s touch has made holy. You’ll
see."

In conclusion the S. C. P. said:
“That is the way the thing came about. Barnum did buy Shakespeare’s house. He paid the price asked, and received the properly attested documents of sale. Then there was an explosion, I can tell you. England rose! That, the birthplace of the master-genius of all the ages and all the climes—that priceless possession of Britain—to be carted out of the country like so much old lumber and set up for sixpenny desecration in a Yankee show-shop—the idea was not to be tolerated for a moment. England rose in her indignation; and Barnum was glad to relinquish his prize and offer apologies. However, he stood out for a compromise; he claimed a concession—England must let him have Jumbo. And England consented, but not cheerfully.”
It shows how, by help of time, a story can grow—even after Barnum has had the first innings in the telling of it. Mr. Barnum told me the story himself, years ago. He said that the permission to buy Jumbo was not a concession; the purchase was made and the animal delivered before the public knew anything about it. Also, that the securing of Jumbo was all the advertisement he needed. It produced many columns of newspaper talk, free of cost, and he was satisfied. He said that if he had failed to get Jumbo he would have caused his notion of buying the Nelson Monument to be treacherously smuggled into print by some trusty friend, and after he had gotten a few hundred pages of gratuitous advertising out of it, he would have come out with a blundering, obtuse, but warm-hearted letter of apology, and in a postscript to it would have naively proposed to let the Monument go, and take Stonehenge in place of it at the same price.
It was his opinion that such a letter, written with well-simulated asinine innocence and gush would have gotten his ignorance and stupidity an amount of newspaper abuse worth six fortunes to him, and not purchasable for twice the money.
I knew Mr. Barnum well, and I placed every confidence in the account which he gave me of the Shakespeare birthplace episode. He said he found the house neglected and going-to decay, and he inquired into the matter and was told that many times earnest efforts had been made to raise money for its proper repair and preservation, but without success. He then proposed to buy it. The proposition was entertained, and a price named—$50,000, I think; but whatever it was, Barnum paid the money down, without remark, and the papers were drawn up and executed. He said that it had been his purpose to set up the house in his Museum, keep it in repair, protect it from name-scribblers and other desecrators, and leave it by bequest to the safe and perpetual guardianship of the Smithsonian Institute at Washington.
But as soon as it was found that Shakespeare’s house had passed into foreign hands and was going to be carried across the ocean, England was stirred as no appeal from the custodians of the relic had ever stirred England before, and protests came flowing in—and money, too, to stop the outrage. Offers of repurchase were made—offers of double the money that Mr. Barnum had paid for the house. He handed the house back, but took only the sum which it had cost him—but on the condition that an endowment sufficient for the future safeguarding and maintenance of the sacred relic should be raised. This condition was fulfilled.
That was Barnum’s account of the episode; and to the end of his days he claimed with pride and satisfaction that not England, but America—represented by him—saved the birthplace of Shakespeare from destruction.
At 3 P.M., May 6th, the ship slowed down, off the land, and thoughtfully
and cautiously picked her way into the snug harbor of Durban, South
Africa.

CHAPTER LXV.
In statesmanship get the formalities right, never mind about the moralities.
—Pudd’nhead Wilson’s New Calendar.
FROM DIARY:
Royal Hotel. Comfortable, good table, good service of natives and Madrasis. Curious jumble of modern and ancient city and village, primitiveness and the other thing. Electric bells, but they don’t ring. Asked why they didn’t, the watchman in the office said he thought they must be out of order; he thought so because some of them rang, but most of them didn’t. Wouldn’t it be a good idea to put them in order? He hesitated—like one who isn’t quite sure—then conceded the point.
May 7. A bang on the door at 6. Did I want my boots cleaned? Fifteen minutes later another bang. Did we want coffee? Fifteen later, bang again, my wife’s bath ready; 15 later, my bath ready. Two other bangs; I forget what they were about. Then lots of shouting back and forth, among the servants just as in an Indian hotel.
Evening. At 4 P.M. it was unpleasantly warm. Half-hour after sunset one needed a spring overcoat; by 8 a winter one.
Durban is a neat and clean town. One notices that without having his attention called to it.
Rickshaws drawn by splendidly built black Zulus, so overflowing with strength, seemingly, that it is a pleasure, not a pain, to see them snatch a rickshaw along. They smile and laugh and show their teeth—a good-natured lot. Not allowed to drink; 2s per hour for one person; 3s for two; 3d for a course—one person.
The chameleon in the hotel court. He is fat and indolent and
contemplative; but is business-like and capable when a fly comes about—reaches
out a tongue like a teaspoon and takes him in. He gums his tongue first.
He is always pious, in his looks. And pious and thankful both, when
Providence or one of us sends him a fly. He has a froggy head, and a back
like a new grave—for shape; and hands like a bird’s toes that have
been frostbitten. But his eyes are his exhibition feature. A couple of
skinny cones project from the sides of his head, with a wee shiny bead of
an eye set in the apex of each; and these cones turn bodily like
pivot-guns and point every-which-way, and they are independent of each
other; each has its own exclusive machinery. When I am behind him and C.
in front of him, he whirls one eye rearwards and the other forwards—which
gives him a most Congressional expression (one eye on the constituency and
one on the swag); and then if something happens above and below him he
shoots out one eye upward like a telescope and the other downward—and
this changes his expression, but does not improve it.

Natives must not be out after the curfew bell without a pass. In Natal there are ten blacks to one white.
Sturdy plump creatures are the women. They comb their wool up to a peak
and keep it in position by stiffening it with brown-red clay—half of
this tower colored, denotes engagement; the whole of it colored denotes
marriage.

None but heathen Zulus on the police; Christian ones not allowed.
May 9. A drive yesterday with friends over the Berea. Very fine roads and lofty, overlooking the whole town, the harbor, and the sea-beautiful views. Residences all along, set in the midst of green lawns with shrubs and generally one or two intensely red outbursts of poinsettia—the flaming splotch of blinding red a stunning contrast with the world of surrounding green. The cactus tree—candelabrum-like; and one twisted like gray writhing serpents. The “flat-crown” (should be flat-roof)—half a dozen naked branches full of elbows, slant upward like artificial supports, and fling a roof of delicate foliage out in a horizontal platform as flat as a floor; and you look up through this thin floor as through a green cobweb or veil. The branches are japanesich. All about you is a bewildering variety of unfamiliar and beautiful trees; one sort wonderfully dense foliage and very dark green—so dark that you notice it at once, notwithstanding there are so many orange trees. The “flamboyant”—not in flower, now, but when in flower lives up to its name, we are told. Another tree with a lovely upright tassel scattered among its rich greenery, red and glowing as a firecoal. Here and there a gum-tree; half a dozen lofty Norfolk Island pines lifting their fronded arms skyward. Groups of tall bamboo.
Saw one bird. Not many birds here, and they have no music—and the flowers not much smell, they grow so fast.
Everything neat and trim and clean like the town. The loveliest trees and the greatest variety I have ever seen anywhere, except approaching Darjeeling. Have not heard anyone call Natal the garden of South Africa, but that is what it probably is.
It was when Bishop of Natal that Colenso raised such a storm in the religious world. The concerns of religion are a vital matter here yet. A vigilant eye is kept upon Sunday. Museums and other dangerous resorts are not allowed to be open. You may sail on the Bay, but it is wicked to play cricket. For a while a Sunday concert was tolerated, upon condition that it must be admission free and the money taken by collection. But the collection was alarmingly large and that stopped the matter. They are particular about babies. A clergyman would not bury a child according to the sacred rites because it had not been baptized. The Hindoo is more liberal. He burns no child under three, holding that it does not need purifying.
The King of the Zulus, a fine fellow of 30, was banished six years ago for a term of seven years. He is occupying Napoleon’s old stand—St. Helena. The people are a little nervous about having him come back, and they may well be, for Zulu kings have been terrible people sometimes—like Tchaka, Dingaan, and Cetewayo.
There is a large Trappist monastery two hours from Durban, over the country roads, and in company with Mr. Milligan and Mr. Hunter, general manager of the Natal government railways, who knew the heads of it, we went out to see it.
There it all was, just as one reads about it in books and cannot believe
that it is so—I mean the rough, hard work, the impossible hours, the
scanty food, the coarse raiment, the Maryborough beds, the tabu of human
speech, of social intercourse, of relaxation, of amusement, of
entertainment, of the presence of woman in the men’s establishment. There
it all was. It was not a dream, it was not a lie. And yet with the fact
before one’s face it was still incredible. It is such a sweeping
suppression of human instincts, such an extinction of the man as an
individual.
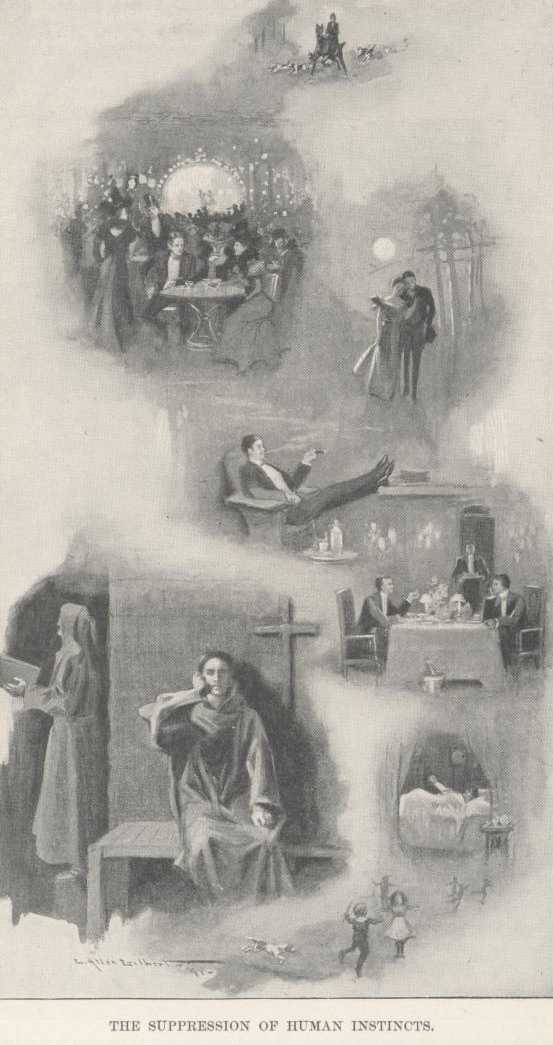

La Trappe must have known the human race well. The scheme which he invented hunts out everything that a man wants and values—and withholds it from him. Apparently there is no detail that can help make life worth living that has not been carefully ascertained and placed out of the Trappist’s reach. La Trappe must have known that there were men who would enjoy this kind of misery, but how did he find it out?
If he had consulted you or me he would have been told that his scheme lacked too many attractions; that it was impossible; that it could never be floated. But there in the monastery was proof that he knew the human race better than it knew itself. He set his foot upon every desire that a man has—yet he floated his project, and it has prospered for two hundred years, and will go on prospering forever, no doubt.
Man likes personal distinction—there in the monastery it is obliterated. He likes delicious food—there he gets beans and bread and tea, and not enough of it. He likes to lie softly—there he lies on a sand mattress, and has a pillow and a blanket, but no sheet. When he is dining, in a great company of friends, he likes to laugh and chat—there a monk reads a holy book aloud during meals, and nobody speaks or laughs. When a man has a hundred friends about him, evenings, he likes to have a good time and run late—there he and the rest go silently to bed at 8; and in the dark, too; there is but a loose brown robe to discard, there are no night-clothes to put on, a light is not needed. Man likes to lie abed late—there he gets up once or twice in the night to perform some religious office, and gets up finally for the day at two in the morning. Man likes light work or none at all—there he labors all day in the field, or in the blacksmith shop or the other shops devoted to the mechanical trades, such as shoemaking, saddlery, carpentry, and so on. Man likes the society of girls and women—there he never has it. He likes to have his children about him, and pet them and play with them—there he has none. He likes billiards—there is no table there. He likes outdoor sports and indoor dramatic and musical and social entertainments—there are none there. He likes to bet on things—I was told that betting is forbidden there. When a man’s temper is up he likes to pour it out upon somebody there this is not allowed. A man likes animals—pets; there are none there. He likes to smoke—there he cannot do it. He likes to read the news—no papers or magazines come there. A man likes to know how his parents and brothers and sisters are getting along when he is away, and if they miss him—there he cannot know. A man likes a pretty house, and pretty furniture, and pretty things, and pretty colors—there he has nothing but naked aridity and sombre colors. A man likes—name it yourself: whatever it is, it is absent from that place.
From what I could learn, all that a man gets for this is merely the saving of his soul.
It all seems strange, incredible, impossible. But La Trappe knew the race. He knew the powerful attraction of unattractiveness; he knew that no life could be imagined, howsoever comfortless and forbidding, but somebody would want to try it.
This parent establishment of Germans began its work fifteen years ago, strangers, poor, and unencouraged; it owns 15,000 acres of land now, and raises grain and fruit, and makes wines, and manufactures all manner of things, and has native apprentices in its shops, and sends them forth able to read and write, and also well equipped to earn their living by their trades. And this young establishment has set up eleven branches in South Africa, and in them they are christianizing and educating and teaching wage-yielding mechanical trades to 1,200 boys and girls. Protestant Missionary work is coldly regarded by the commercial white colonist all over the heathen world, as a rule, and its product is nicknamed “rice-Christians” (occupationless incapables who join the church for revenue only), but I think it would be difficult to pick a flaw in the work of these Catholic monks, and I believe that the disposition to attempt it has not shown itself.
Tuesday, May 12. Transvaal politics in a confused condition. First the
sentencing of the Johannesburg Reformers startled England by its severity;
on the top of this came Kruger’s exposure of the cipher correspondence,
which showed that the invasion of the Transvaal, with the design of
seizing that country and adding it to the British Empire, was planned by
Cecil Rhodes and Beit—which made a revulsion in English feeling, and
brought out a storm against Rhodes and the Chartered Company for degrading
British honor. For a good while I couldn’t seem to get at a clear
comprehension of it, it was so tangled. But at last by patient study I
have managed it, I believe. As I understand it, the Uitlanders and other
Dutchmen were dissatisfied because the English would not allow them to
take any part in the government except to pay taxes. Next, as I understand
it, Dr. Kruger and Dr. Jameson, not having been able to make the medical
business pay, made a raid into Matabeleland with the intention of
capturing the capital, Johannesburg, and holding the women and children to
ransom until the Uitlanders and the other Boers should grant to them and
the Chartered Company the political rights which had been withheld from
them. They would have succeeded in this great scheme, as I understand it,
but for the interference of Cecil Rhodes and Mr. Beit, and other Chiefs of
the Matabele, who persuaded their countrymen to revolt and throw off their
allegiance to Germany. This, in turn, as I understand it, provoked the
King of Abyssinia to destroy the Italian army and fall back upon
Johannesburg; this at the instigation of Rhodes, to bull the stock market.