
Facsimile of a part of Despujol’s private inquiry of Executive Secretary de la Torre.
This inquiry is joined to an order to the local authorities in the provinces near Manila instructing them to watch the comings and goings of their prominent people Page 181during the following weeks. The scheme resembled that which was concocted prior to ’72, but Governor-General de la Torte was honest in his reforms. Despujol may, or may not, have been honest in other matters, but as concerns Rizal there is no lack of proof of his perfidy. The confidential file relating to this part of the case was forgotten in destroying and removing secret papers when Manila passed into a democratic conqueror’s hands, and now whoever wishes may read, in the Bureau of Archives, documents which the Conde de Caspe, to use a noble title for an ignoble man, considered safely hidden. As with Page 182Weyler’s contidential letter to the friar landlords, these discoveries convict their writers of bad faith, with no possibility of mistake.

Case secretly filed against Rizal.
This point in the reformed Spanish writer’s biography of Rizal is made occasion for another of his treacherous attacks upon the good name of his pretended hero. Just as in the land troubles Retana held that legally Governor-General Weyler was justified in disregarding an appeal pending in the courts, so in this connection he declares: ”(Despujol) unquestionably had been deceived by Rizal when, from Hongkong, he offered to Despujol not to meddle in politics.” That Rizal meddled in politics rests solely upon Despujol’s word, and it will be seen later how little that is worth; but, politics or no politics, Rizal’s fate was settled before he ever came to Manila.
|
Luis de la Torre, Secretary to Despujol. |
Rizal was accompanied to Manila by his sister Lucia, widow of that brother-in-law who had been denied Christian burial because of his relationship to Rizal. In the Basa home, among other waste papers, and for that use, she had gathered up five copies of a recent “proclamation,” entitled “Pobres Frailes” (Poor Friars), a small sheet possibly two inches wide and five long. These, crumpled up, were tucked into the case of the pillow which Mrs. Hervosa used on board. Later, rolled up in her blankets and bed mat, or petate, they went to the custom house along with the other baggage, and of course were discovered in the rigorous examination which the officers always made. How strict Philippine customs searches were, Henry Norman, an English writer of travels, explains Page 183by remarking that Manila was the only port where he had ever had his pockets picked officially. His visit was made at about the time of which we are writing, and the object, he says, was to keep out anti friar publications.
Rizal and his sister landed without difficulty, and he at once went to the Oriente Hotel, then the best in town, for Rizal always traveled and lived as became a member of a well-to-do family. Next he waited on the Governor-General, with whom he had a very brief interview, for it happened to be on one of the numerous religious festivals, during which he obtained favorable consideration for his deported sisters. Several more interviews occurred in which the hopes first given were realized, so that those of the family then awaiting exile were pardoned and those already deported were to be returned at an early date.
One night Rizal was the guest of honor at a dinner given by the masters and wardens of the Masonic lodges of Manila, and he was surprised and delighted at the progress the institution had made in the Islands. Then he had another task not so agreeable, for, while awaiting a delayed appointment with the Governor-General, he with two others ran up on the new railway to Tarlac. Ostensibly this was to see the country, but it was not for a pleasure trip. They were investigating the sales of Rizal’s books and trying to find out what had become of the money received from them, for while the author’s desire had been to place them at so low a price as to be within the reach of even the poor, it was reported that the sales had been few and at high prices, so that copies were only read by the wealthy whose desire to obtain the rare and much-discussed novels led them to pay exorbitant figures for them.
Rizal’s party, consisting of the Secretary of one of the lodges of Manila, and another Mason, a prominent school-teacher, were under constant surveillance and a Page 184minute record of their every act is preserved in the “reserved” files, now, of course, so only in name, as they are no longer secret. Immediately after they left a house it would be thoroughly searched and the occupants strictly questioned. In spite of the precautions of the officials, Rizal soon learned of this, and those whom they visited were warned of what to expect. In one home so many forbidden papers were on hand that Rizal delayed his journey till the family completed their task of carrying them upstairs and hiding them in the roof.
At another place he came across an instance of superstition such as that which had caused him to cease his sleight-of-hand exhibitions on his former return to the Islands. Their host was a man of little education but great hospitality, and the party were most pleasantly entertained. During the conversation he spoke of Rizal, but did not seem to know that his hero had come back to the Philippines. His remarks drifted into the wildest superstition, and, after asserting that Rizal bore a charmed life, he startled his audience by saying that if the author of “Noli Me Tangere” cared to do so, he could be with them at that very instant. At first the three thought themselves discovered by their host, but when Rizal made himself known, the old man proved that he had had no suspicion of his guest’s identity, for he promptly became busy preparing his home for the search which he realized would shortly follow. On another occasion their host was a stranger whom Rizal treated for a temporary illness, leaving a prescription to be filled at the drug store. The name signed to the paper was a revelation, but the first result was activity in cleaning house.
No fact is more significant of the utter rottenness of the Spanish rule than the unanimity of the people in their discontent. Only a few persons at first were in open opposition, but books, pamphlets and circulars were eagerly Page 185sought, read and preserved, with the knowledge generally, of the whole family, despite the danger of possessing them. At times, as in the case of Rizal’s novels, an entire neighborhood was in the secret; the book was buried in a garden and dug up to be read from at a gathering of the older men, for which a dance gave pretext. Informers were so rare that the possibility of treachery among themselves was hardly reckoned in the risk.
The authorities were constantly searching dwellings, often entire neighborhoods, and with a thoroughness which entirely disregarded the possibility of damaging an innocent person’s property. These “domiciliary registrations” were, of course, supposed to be unexpected, but in the later Spanish days the intended victims usually had warning from some employee in the office where it was planned, or from some domestic of the official in charge; very often, however, the warning was so short as to give only time for a hasty destruction of incriminating documents and did not permit of their being transferred to other hiding places. Thus large losses were incurred, and to these must be added damages from dampness when a hole in the ground, the inside of a post, or cementing up in the wall furnished the means of concealment. Fires, too, were frequent, and such events attracted so much attention that it was scarcely safe to attempt to save anything of an incriminating nature.
Six years of war conditions did their part toward destroying what little had escaped, and from these explanations the reader may understand how it comes that the tangled story of Spain’s last half century here presents an historical problem more puzzling than that of much more remote times in more favored lands.
It seems almost providential that the published statement of the Governor-General can be checked not only by an account which Rizal secretly sent to friends, but Page 186also by the candid memoranda contained in the untruthful executive’s own secret folios. While some unessential details of Rizal’s career are in doubt, not a point vital to establishing his good name lacks proof that his character was exemplary and that he is worthy of the hero-worship which has come to him.
After Rizal’s return to Manila from his railway trip he had the promised interview with the Governor-General. At their previous meetings the discussions had been quite informal. Rizal, in complimenting the General upon his inauguration of reforms, mentioned that the Philippine system of having no restraint whatever upon the chief executive had at least the advantage that a well-disposed governor-general would find no red-tape hindrances to his plans for the public benefit. But Despujol professed to believe that the best of men make mistakes and that a wise government would establish safeguards against this human fallibility.
The final, and fatal, interview began with the Governor-General asking Rizal if he still persisted in his plan for a Filipino colony in British North Borneo; Despujol had before remarked that with so much Philippine land lying idle for want of cultivation it did not seem to him patriotic to take labor needed at home away for the development of a foreign land. Rizal’s former reply had dealt with the difficulty the government was in respecting the land troubles, since the tenants who had taken the old renters’ places now also must be considered, and he pointed out that there was, besides, a bitterness between the parties which could not easily be forgotten by either side. So this time he merely remarked that he had found no reason for changing his original views.
Hereupon the General took from his desk the five little sheets of the “Poor Friars” handbill, which he said had been found in the roll of bedding sent with Rizal’s baggage Page 187to the custom house, and asked whose they could be. Rizal answered that of course the General knew that the bedding belonged to his sister Lucia, but she was no fool and would not have secreted in a place where they were certain to be found five little papers which, hidden within her camisa or placed in her stocking, would have been absolutely sure to come in unnoticed.
Rizal, neither then nor later, knew the real truth, which was that these papers were gathered up at random and without any knowledge of their contents. If it was a crime to have lived in a house where such seditious printed matter was common, then Rizal, who had openly visited Basa’s home, was guilty before ever the handbills were found. But no reasonable person would believe another rational being could be so careless of consequences as to bring in openly such dangerous material.
The very title was in sarcastic allusion to the inconsistency of a religious order being an immensely wealthy organization, while its individual members were vowed to poverty. News, published everywhere except in the Philippines, of losses sustained in outside commercial enterprises running into the millions, was made the text for showing how money, professedly raised in the Philippines for charities, was not so used and was invested abroad in fear of that day of reckoning when tyranny would be overthrown in anarchy and property would be insecure. The belief of the pious Filipinos, fostered by their religious exploiters, that the Pope would suffer great hardship if their share of “Peter’s pence” was not prompt and full, was contrasted with another newspaper story of a rich dowry given to a favorite niece by a former Pope, but that in no way taught the truth that the Head of the Church was not put to bodily discomfort whenever a poor Filipino failed to come forward with his penny.
Page 188Despujol managed to work himself into something like a passion over this alleged disrespect to the Pope, and ordered Rizal to be taken as a prisoner to Fort Santiago by the nephew who acted as his aide.
Like most facts, this version runs a middle course between the extreme stories which have been current. Like circulars may have been printed at the “Asilo de Malabon,” as has been asserted; these certainly came from Hongkong and were not introduced by any archbishop’s nephew on duty at the custom house, as another tale suggests. On the other hand, the circular was the merest pretext, and Despujol did not act in good faith, as many claim that he did.
It may be of interest to reprint the handbill from a facsimile of an original copy:
Pobres Frailes!
Acaba de suspender sus pages un Banco, acaba de quebrarse el New Oriental.
Grandes pédidas en la India, en la isla Mauricio al sur de Africa, ciclónes y tempestades acabaron con su podeíro, tragnádose más de 36,000,000 de pesos. Estos treinta y seis millones representaban las esperanzas, las economías, el bienestar y el porvenir de numerosos individuos y familias.
Entre los que más han sufrido podemos contar á la Rvda. Corporacion de los P. P. Dominicos, que pierden en esta quiebra muchos cientos de miles. No se sabe la cuenta exacta porque tanto dinero se les envía de aquí y tantos depósitos hacen, que se neçesitarlan muchos contadores para calcular el immense caudal de que disponen.
Pero, no se aflijan los amigos ni triunfen los enemigos de los santos monjes que profesan vote de pobreza.
A unos y otros les diremos que pueden estar tranquilos. La Corporacion tiene aun muchos millones depositados en los Bancos de Hongkong, y aunque todos quebrasen, y aunque se derrumbasen sus miles de casas de alquiler, siempre quedarian sus curates y Page 189haciendas, les quedarían los filipinos dispuestos siempre á ayunar para darles una limosna. ¿Qué son cuatrocientos ó quinientos mil? Que se tomen la molestia de recorrer los pueblos y pedir limosna y se resarcirán de esa pérdida. Hace un año que, por la mala administracion de los cardenales, el Papa perdió 14,000,000 del dinero de San Pedro; el Papa, para cubrir el déficit, acude á nosotros y nosotros recogemos de nuestros tampipis el último real, porque sabemos que el Papa tiene muchas atenciones; hace cosa de cinco años casó á una sobrina suya dotándola de un palacio y 300,000 francos ademas. Haced un esfuerzo pues, generosos filipinos, y socorred á los dominicos igualmente!
Además, esos centanares de miles perdidos no son de ellos, segun dicen: ¿cómo los iban à tener si tienen voto de pobreza? Hay que creerlos pues cuando, para cubrirse, dicen que son de los huérfanos y de las viudas. Muy seguramente pertencerían algunos á las viudas y á los huérfanos de Kalamba, y quién sabe si á los desterrados maridos! y los manejan los virtuosos frailes sólo á título de depositarios para devolverlos despues religiosamente con todos sus intereses cuando llegue el día de rendir cuentas! Quién sabe? Quién mejor que ellos podía encargarse de recoger los pocos haberes mientras las casas ardían, huían las viudas y los huérfanos sin encontrar hospitalidad, pues se habia prohibido darles albergue, mientras los hombres estaban presos ó perseguidos? ¿Quién mejor que los dominicos para tener tanto valor, tanta audacia y tanta humanidad?
Pero, ahora el diablo se ha llevado el dinero de los huérfanos y de las viudas, y es de temer que se lleve tambien el resto, pues cuando el diablo la empieza la ha de acabar. Tendría ese dinero mala procedencia?
Si asl sucediese, nosotros los recomendaríamos á los dominicos que dijesen con Job: Desnudo salí del vientre de mi madre (España), y desnudo volveré allá; lo dió el diablo, el diablo se lo llevó; bendito sea el nombre del Señor!
Fr. Jacinto.
Manila: Imprenta de los Amigos del Pais.
Chapter IX
The Deportation to Dapitan
As soon as Rizal was lodged in his prison, a room in Fort Santiago, the Governor-General began the composition of one of the most extraordinary official documents ever issued in this land where the strangest governmental acts have abounded. It is apology, argument, and attack all in one and was published in the Official Gazette, where it occupied most of an entire issue. The effect of the righteous anger it displays suffers somewhat when one knows how all was planned from the day Rizal was decoyed from Hongkong under the faithless safe-conduct. Another enlightening feature is the copy of a later letter, preserved in that invaluable secret file, wherein Despujol writes Rizal’s custodian, as jailer, to allow the exile in no circumstances to see this number of the Gazette or to know its contents, and suggests several evasions to assist the subordinate’s power of invention. It is certainly a strange indignation which fears that its object shall learn the reason for wrath, nor is it a creditable spectacle when one beholds the chief of a government giving private lessons in lying.
A copy of the Gazette was sent to the Spanish Consul in Hongkong, also a cablegram directing him to give it publicity that “Spain’s good name might not suffer” in that colony. By his blunder, not knowing that the Lusitania Club was really a Portuguese Masonic lodge and full of Rizal’s friends, a copy was sent there and a strong reply was called forth. The friendly editor of the Hongkong Telegraph devoted columns to the outrage by which a man whose acquaintance in the scientific world reflected honor upon his nation, was decoyed to what was intended to be his death, exiled to “an unhealthful, savage Page 191Page 192spot,” through “a plot of which the very Borgias would have been ashamed.”

Regulations of La Liga Filipina in Rizal’s handwriting.
(Facsimile.)
The British Consul in Manila, too, mentioned unofficially to Governor-General Despujol that it seemed a strange way of showing Spain’s often professed friendship for Great Britain thus to disregard the annoyance to the British colony of North Borneo caused by making impossible an entirely unexceptionable plan. Likewise, in much the same respectfully remonstrant tone which the Great Powers are wont to use in recalling to semi-savage states their obligations to civilization, he pointed out how Spain’s prestige as an advanced nation would suffer when the educated world, in which Rizal was Spain’s best-known representative, learned that the man whom they honored had been trapped out of his security under the British flag and sent into exile without the slightest form of trial.
Almost the last act of Rizal while at liberty was the establishment of the “Liga Filipina,” a league or association seeking to unite all Filipinos of good character for concerted action toward the economic advancement of their country, for a higher standard of manhood, and to assure opportunities for education and development to talented Filipino youth. Resistance to oppression by lawful means was also urged, for Rizal believed that no one could fairly complain of bad government until he had exhausted and found unavailing all the legal resources provided for his protection. This was another expression of his constant teaching that slaves, those who toadied to power, and men without self-respect made possible and fostered tyranny, abuses and disregard of the rights of others.
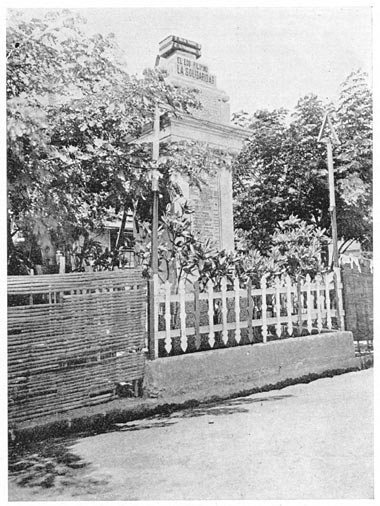
The Calle Ilaya monument to Rizal and his associates of La Liga Filipina.
The character test was also a step forward, for the profession of patriotism has often been made to cloak moral shortcomings in the Philippines as well as elsewhere. Page 193Rizal urged that those who would offer themselves on the altar of their fatherland must conform to the standard of old, and, like the sacrificial lamb, be spotless and without blemish. Therefore, no one who had justifiably Page 194been prosecuted for any infamous crime was eligible to membership in the new organization.
The plan, suggested by a Spanish Masonic society called C. Kadosch y Cia., originated with José Maria Basa, at whose instance Rizal drafted the constitution and regulations. Possibly all the members were Freemasons of the educated and better-to-do class, and most of them adhered to the doctrine that peaceably obtained reforms and progress by education are surest and best.
Rizal’s arrest discouraged those of this higher faith, for the peaceable policy seemed hopeless, while the radical element, freed from Rizal’s restraining influence and deeming the time for action come, formed a new and revolutionary society which preached force of arms as the only argument left to them, and sought its membership among the less-enlightened and poorer class.
Their inspiration was Andrés Bonifacio, a shipping clerk for a foreign firm, who had read and re-read accounts of the French Revolution till he had come to believe that blood alone could wipe out the wrongs of a country. His organization, The Sons of the Country, more commonly called the Katipunan, was, however, far from being as bloodthirsty as most Spanish accounts, and those of many credulous writers who have got their ideas from them, have asserted. To enlist others in their defense, those who knew that they were the cause of dissatisfaction spread the report that a race war was in progress and that the Katipuneros were planning the massacre of all of the white race. It was a sufficiently absurd statement, but it was made even more ridiculous by its “proof,” for this was the discovery of an apron with a severed head, a hand holding it by the hair and another grasping the dagger which had done the bloody work. This emblem, handed down from ancient days as an object lesson of faithfulness even to death, has been Page 195known in many lands besides the Philippines, but only here has it ever been considered anything but an ancient symbol. As reasonably might the paintings of martyrdoms in the convents be taken as evidence of evil intentions upon the part of their occupants, but prejudice looks for pretexts rather than reasons, and this served as well as any other for the excesses of which the government in its frenzy of fear was later guilty.
In talking of the Katipunan one must distinguish the first society, limited in its membership, from the organization of the days of the Aguinaldo “republic,” so called, when throughout the Tagalog provinces, and in the chief towns of other provinces as well, adherence to the revolutionary government entailed membership in the revolutionary society. And neither of these two Katipunans bore any relation, except in name and emblems, to the robber bands whose valor was displayed after the war had ceased and whose patriotism consisted in wronging and robbing their own defenseless countrymen and countrywomen, while carefully avoiding encounters with any able to defend themselves.
Rizal’s arrest had put an end to all hope of progress under Governor-General Despujol. It had left the political field in possession of those countrymen who had not been in sympathy with his campaign of education. It had caused the succession of the revolutionary Katipunan to the economic Liga Filipina, with talk of independence supplanting Rizal’s ambition for the return of the Philippines to their former status under the Constitution of Cadiz. But the victim of the arrest was at peace as he had not been in years. The sacrifice for country and for family had been made, but it was not to cost him life, and he was human enough to wish to live. A visitor’s room in the Fort and books from the military library made his detention comfortable, for he did not worry Page 196about the Spanish sentries without his door who were placed there under orders to shoot anyone who might attempt to signal to him from the plaza.
One night the Governor-General’s nephew-aide came again to the Fort and Rizal embarked on the steamer which was to take him to his place of exile, but closely as he was guarded he risked dropping a note which a Filipino found and took, as it directed, to Mrs. Rizal’s cousin, Vicenta Leyba, who lived in Calle José, Trozo. Thus the family were advised of his departure; this incident shows Rizal’s perfect confidence in his countrymen and the extent to which it was justified; he could risk a chance finder to take so dangerous a letter to its address.
On the steamer he occupied an officer’s cabin and also found a Filipino quartermaster, of whom he requested a life preserver for his stateroom; evidently he was not entirely confident that there were no hostile designs against him. Accidents had rid the Philippines of troublesome persons before his time, and he was determined that if he sacrificed his life for his country, it should be openly. He realized that the tree of Liberty is often watered with the blood of secret as well as open martyrs.
The same boat carried some soldier prisoners, one of whom was to be executed in Mindanao, and their case was not particularly creditable to Spanish ideas of justice. A Spanish officer had dishonorably interfered with the domestic relations of a sergeant, also Spanish, and the aggrieved party had inflicted punishment upon his superior, with the help of some other soldiers. For allowing himself to be punished, not for his own disgraceful act, the officer was dismissed from the service, but the sergeant was to go to the scene of his alleged “crime,” there to suffer death, while his companions who had assisted him in protecting their homes were to be witnesses of this “justice” and then to be imprisoned.
Page 197After an uneventful trip the steamer reached Dapitan, in the northeast of the large island of Mindanao, on a dark and rainy evening. The officer in charge of the expedition took Doctor Rizal ashore with some papers relating to him and delivered all to the commandant, Ricardo Carnicero. The receipt taken was briefed “One countryman and two packages.” At the same time learned men in Europe were beginning to hear of this outrage worthy of the Dark Ages and were remarking that Spain had stopped the work of the man who was practically her only representative in modern science, for the Castilian language has not been the medium through which any considerable additions have been made to the world’s store of scientific knowledge.
Rizal was to reside either with the commandant or with the Jesuit parish priest, if the latter would take him into the convento. But while the exile had learned with pleasure that he was to meet priests who were refined and learned, as well as associated with his happier school days, he did not know that these priests were planning to restore him to his childhood faith and had mapped out a plan of action which should first make him feel his loneliness. So he was denied residence with the priest unless he would declare himself genuinely in sympathy with Spain.
On his previous brief visit to the Islands he had been repelled from the Ateneo with the statement that till he ceased to be anti-Catholic and anti-Spanish he would not be welcome. Padre Faura, the famous meteorologist, was his former instructor and Rizal was his favorite pupil; he had tearfully predicted that the young man would come to the scaffold at last unless he mended his ways. But Rizal, confident in the clearness of his own conscience, went out cheerfully, and when the porter tried to bring back the memory of his childhood piety by reminding him of the image of the Sacred Heart which Page 198he had carved years before, Rizal answered, “Other times, other customs, Brother. I do not believe that way any more.”
So Rizal, a good Catholic, was compelled to board with the commandant instead of with the priest because he was unwilling to make hypocritical professions of admiration for Spain. The commandant and Rizal soon became good friends, but in order to retain his position Carnicero had to write to the Governor-General in a different strain.
The correspondence tells the facts in the main, but of course they are colored throughout to conform to Despujol’s character. The commandant is always represented as deceiving his prisoner and gaining his confidence only to betray him, but Rizal seems never to have experienced anything but straightforward dealing.
Rizal’s earliest letter from Dapitan speaks almost enthusiastically of the place, describing the climate as exceptional for the tropics, his situation as agreeable, and saying that he could be quite content if his family and his books were there.
Shortly after occurred the anniversary of Carnicero’s arrival in the town, and Rizal celebrated the event with a Spanish poem reciting the improvements made since his coming, written in the style of the Malay loa, and as though it were by the children of Dapitan.
Next Rizal acquired a piece of property at Talisay, a little bay close to Dapitan, and at once became interested in his farm. Soon he built a house and moved into it, gathering a number of boy assistants about him, and before long he had a school. A hospital also was put up for his patients and these in time became a source of revenue, as people from a distance came to the oculist for treatment and paid liberally.

Three new Species discovered by Rizal and named after him.
One five-hundred-peso fee from a rich Englishman was Page 199devoted by Rizal to lighting the town, and the community benefited in this way by his charity in addition to the free treatment given its poor. Page 200

Specimens collected by Rizal and Father Sanchez, now in the Jesuit Museum.
The little settlement at Talisay kept growing and those who lived there were constantly improving it. When Father Obach, the Jesuit priest, fell through the bamboo stairway in the principal house, Rizal and his boys burned shells, made mortar, and soon built a fine stone stairway. They also did another piece of masonry work in the Page 201shape of a dam for storing water that was piped to the houses and poultry yard; the overflow from the dam was made to fill a swimming tank.

The mother’s revenge. Statuette modelled by Rizal in 1894.
The school, including the house servants, numbered about twenty and was taught without books by Rizal, who conducted his recitations from a hammock. Considerable importance was given to mathematics, and in languages English was taught as well as Spanish, the entire waking period being devoted to the language allotted for the day, and whoever so far forgot as to utter a word in any other tongue was punished by having to wear a rattan handcuff. The use and meaning of this modern police device had to be explained to the boys, for Spain still tied her prisoners with rope.
|
Father Sanchez, S. J. |
Nature study consisted in helping the Doctor gather specimens of flowers, shells, insects and reptiles which were prepared and shipped to German museums. Rizal was paid for these specimens by scientific books and material. The director of the Royal Zoölogical and Anthropological Museum in Dresden, Saxony, Doctor Karl von Heller, was a great friend and admirer of Doctor Rizal. Doctor Heller’s father was tutor to the late King Alfonso XII and had many friends at the Court of Spain. Evidently Doctor Heller and other of his European friends did not consider Rizal a Spanish insurrectionary, but treated him rather as a reformer seeking progress by peaceful means.
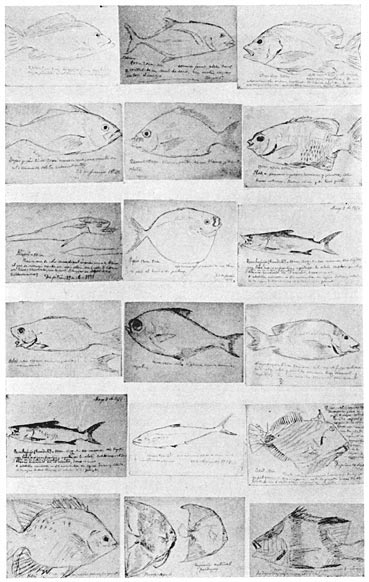
Facsimile of Rizal’s drawings of fishes caught at Dapitan.
Doctor Rizal remunerated his pupils’ work with gifts Page 202Page 203of clothing, books and other useful remembrances. Sometimes the rewards were cartidges, and those who had accumulated enough were permitted to accompany him in his hunting expeditions. The dignity of labor was practically inculcated by requiring everyone to make himself useful, and this was really the first school of the type, combining the use of English, nature study and industrial instruction.
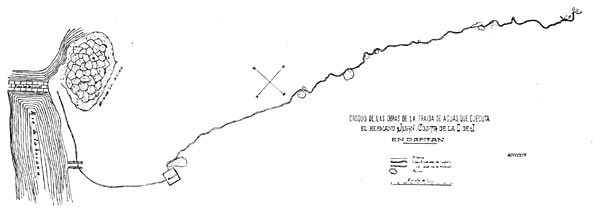
Plan of the waterworks for Dapitan constructed by Dr. Rizal and the Jesuit lay brother Juan Costa. Rizal’s name was omitted for political reasons.
On one occasion in the year 1894 some of his schoolboys secretly went into the town in a banca; a puppy which tried to follow them was eaten by a crocodile. Rizal tired to impress the evil effects of disobedience upon the youngsters by Page 204pointing out to them the sorrow which the mother-dog felt at the loss of her young one, and emphasized the lesson by modeling a statuette called “The Mother’s Revenge,” wherein she is represented, in revenge, as devouring the cayman. It is said to be a good likeness of the animal which was Doctor Rizal’s favorite companion in his many pedestrian excursions around Dapitan.
Father Francisco Sanchez, Rizal’s instructor in rhetoric in the Ateneo, made a long visit to Dapitan and brought with him some surveyor’s instruments, which his former pupil was delighted to assist him in using. Together they ran the levels for a water system for the the town, which was later, with the aid of the lay Jesuit, Brother Tildot, carried to completion. This same water system is now being restored and enlarged with artesian wells by the present insular, provincial and municipal governments jointly, as part of the memorial to Rizal in this place of his exile.
|
Jewelry of earliest Moro converts found by Father Sanchez and Rizal. |
A visit to a not distant mountain and some digging in a spot supposed by the people of the region to be haunted brought to light curious relics of the first Christian converts among the early Moros.
The state of his mind at about this period of his career is indicated by the verses written in his home in Talisay, entitled “My Retreat,” of which the following translation has been made by Mr. Charles Derbyshire. The scene that inspired this poem has been converted by the government into a public park to the memory of Rizal. Page 205

Sketch by Rizal of the hill and excavations where the jewelry was found.
My Retreat
By the spreading beach where the sands are soft and fine,
At the foot of the mount in its mantle of green,
I have built my hut in the pleasant grove’s confine;
From the forest seeking peace and a calmness divine,
Rest for the weary brain and silence to my sorrow keen.
Its roof the frail palm-leaf and its floor the cane,
Its beams and posts of the unhewn wood;
Little there is of value in this hut so plain,
And better by far in the lap of the mount to have lain,
By the song and the murmur of the high sea’s flood.
A purling brook from the woodland glade
Drops down o’er the stones and around it sweeps,
Whence a fresh stream is drawn by the rough cane’s aid;
That in the still night its murmur has made,
And in the day’s heat a crystal fountain leaps.
When the sky is serene how gently it flows,
And its zither unseen ceaselessly plays;
But when the rains fall a torrent it goes
Boiling and foaming through the rocky close,
Roaring uncheck’d to the sea’s wide ways.
The howl of the dog and the song of the bird,
And only the kalao’s hoarse call resound;
Nor is the voice of vain man to be heard,
My mind to harass or my steps to begird;
The woodlands alone and the sea wrap me round.
The sea, ah, the sea! for me it is all,
As it massively sweeps from the worlds apart;
Its smile in the morn to my soul is a call,
And when in the even my fath seems to pall,
It breathes with its sadness an echo to my heart.
By night an arcanum; when translucent it glows,
All spangled over with its millions of lights,
And the bright sky above resplendent shows;
While the waves with their sighs tell of their woes—
Tales that are lost as they roll to the heights.
They tell of the world when the first dawn broke,
And the sunlight over their surface played;
When thousands of beings from nothingness woke,
To people the depths and the heights to cloak,
Wherever its life-giving kiss was laid.
But when in the night the wild winds awake,
And the waves in their fury begin to leap,
Through the air rush the cries that my mind shake;
Voices that pray, songs and moans that partake
Of laments from the souls sunk down in the deep.
Then from their heights the mountains groan,
And the trees shiver tremulous from great unto least;
The groves rustle plaintive and the herds utter moan,
For they say that the ghosts of the folk that are gone
Are calling them down to their death’s merry feast.
In terror and confusion whispers the night,
While blue and green flames flit over the deep;
But calm reigns again with the morning’s light,
And soon the bold fisherman comes into sight,
As his bark rushes on and the waves sink to sleep.
So onward glide the days in my lonely abode;
Driven forth from the world where once I was known,
I muse o’er the fate upon me bestow’d;
A fragment forgotten that the moss will corrode,
To hide from mankind the world in me shown.
I live in the thought of the lov’d ones left,
And oft their names to my mind are borne;
Some have forsaken me and some by death are reft;
But now ’tis all one, as through the past I drift,
That past which from me can never be torn.
For it is the friend that is with me always,
That ever in sorrow keeps the faith in my soul;
While through the still night it watches and prays,
As here in my exile in my lone hut it stays,
To strengthen my faith when doubts o’er me roll.
That faith I keep and I hope to see shine
The day when the Idea prevails over might;
When after the fray and death’s slow decline,
Some other voice sounds, far happier than mine,
To raise the glad song of the triumph of right.
I see the sky glow, refulgent and clear,
As when it forced on me my first dear illusion;
I feel the same wind kiss my forehead sere,
And the fire is the same that is burning here
To stir up youth’s blood in boiling confusion.
I breathe here the winds that perchance have pass’d
O’er the fields and the rivers of my own natal shore;
And mayhap they will bring on the returning blast
The sighs that lov’d being upon them has cast—
Messages sweet from the love I first bore.
To see the same moon, all silver’d as of yore,
I feel the sad thoughts within me arise;
The fond recollections of the troth we swore,
Of the field and the bower and the wide seashore,
The blushes of joy, with the silence and sighs.


