Bilibid Prison.
While the officials were looking for his sack of gold, Alberto gave a power of attorney to an overintelligent lawyer who worded his authority so that it gave him the right to do everything which his principal himself could have done “personally, legally and ecclesiastically.” From some source outside, but not from the brother, the attorney Page 90heard that Mrs. Rizal had had money belonging to Alberto, for in the extensive sugar-purchasing business which she carried on she handled large sums and frequently borrowed as much as five thousand pesos from this brother. Anxious to get his hands on money, he instituted a charge of theft against her, under his power of attorney and acting in the name of his principal. Mrs. Rizal’s attorney demurred to such a charge being made without the man who had lent the money being at all consulted, and held that a power of attorney did not warrant such an action. In time the intelligent Supreme Court heard this case and decided that it should go to trial; but later, when the attorney, acting for his principal, wanted to testify for him under the power of attorney, they seem to have reached their limit, for they disapproved of that proposal.
Anyone who cares to know just how ridiculous and inconsistent the judicial system of the Philippines then was would do well to try to unravel the mixed details of the half dozen charges, ranging from cruelty through theft to murder, which were made against Mrs. Rizal without a shadow of evidence. One case was trumped up as soon as another was finished, and possibly the affair would have dragged on till the end of the Spanish administration had not her little daughter danced before the Governor-General once when he was traveling through the country, won his approval, and when he asked what favor he could do for her, presented a petition for her mother’s release. In this way, which recalls the customs of primitive nations, Mrs. Rizal finally was enabled to return to her home.

Model of head of a Dapitan girl by Rizal.
Doctor Rizal tells us that it was then that he first began to lose confidence in mankind. A story of a school companion, that when Rizal recalled this incident the red came into his eyes, probably has about the same foundation as the frequent stories of his weeping with emotion upon other people’s shoulders when advised of momentous Page 91Page 92changes in his life. Doctor Rizal did not have these Spanish ways, and the narrators are merely speaking of what other Spaniards would have done, for self-restraint and freedom from exhibitions of emotion were among his most prominent characteristics.
Some time during Rizal’s early years of school came his first success in painting. It was the occasion of a festival in Kalamba; just at the last moment an important banner was accidentally damaged and there was not time to send to Manila for another. A hasty consultation was held among the village authorities, and one councilman suggested that José Rizal had shown considerable skill with the brush and possibly he could paint something that would pass. The gobernadorcillo proceeded to the lad’s home and explained the need. Rizal promptly went to work, under the official’s direction, and speedily produced a painting which the delighted municipal executive declared was better than the expensive banner bought in Manila. The achievement was explained to all the participants in the festival and young José was the hero of the occasion.
During intervals of school work Rizal found time to continue his modeling in clay which he procured from the brickyard of a cousin at San Pedro Macati.
Rizal’s uncle, José Alberto, had played a considerable part in his political education. He was influential with the Regency in Spain, which succeeded Queen Isabel when that sovereign became too malodorous to be longer tolerated, and he was the personal friend of the Regent, General Prim, whose motto, “More liberal today than yesterday, more liberal tomorrow than today,” he was fond of quoting. He was present in Madrid at the time of General Prim’s assassination and often told of how this wise patriot, recognizing the unpreparedness of the Spanish people for a republic, opposed the efforts for Page 93what would, he knew, result in as disastrous a failure as had been France’s first effort, and how he lost his life through his desire to follow the safer course of proceeding gradually through the preparatory stage of a constitutional monarchy. Alberto was made by him a Knight of the Order of Carlos III, and, after Prim’s death, was created by King Amadeo a Knight Commander, the step higher in the Order of Isabel the Catholic.
|
Memorial to José Alberto in the church at Biñan. |
Events proved Prim’s wisdom, as Alberto was careful to observe, for King Amadeo was soon convinced of the unfitness of his people for even a constitutional monarchy, told them so, resigned his throne, and bade them farewell. Then came a republic marked by excesses such as even the worst monarch had not committed; among them the dreadful massacre of the members of the filibustering party on the steamer Virginius in Cuba, which would have caused war with the United States had not the Americans been deluded into the idea that they were dealing with a sister republic. America and Switzerland had been the only nations which Page 94had recognized Spain’s new form of government. Prim sought an alliance with America, for he claimed that Spain should be linked with a country which would buy Spanish goods and to which Spain could send her products. France, with whom the Bourbons wished to be allied, was a competitor along Spain’s own lines.
During the earlier disturbances in Spain a party of Carlists were sent to the Philippine Islands; they were welcomed by the reactionary Spaniards, for devotion to King Carlos had been their characteristic ever since the days when Queen Isabel had taken the throne that in their opinion belonged to the heir in the male line. Rizal frequently makes mention of this disloyalty to the ruler of Spain on the part of those who claimed to be most devoted Spaniards.
Along with the stories of these troubles which Rizal heard during his school days in Manila were reports of how these exiles had established themselves in foreign cities, Basa in Hongkong, Regidor in London, and Tavera in Paris. At their homes in these cities they gave a warm welcome to such Filipinos as traveled abroad and they were always ready to act as guardians for Filipino students who wished to study in their cities, Many availed themselves of these opportunities and it came to be an ambition among those in the Islands to get an education which they believed was better than that which Spain afforded. There was some ground for such a belief, because many of the most prominent successful men of Spanish and Philippine birth were men whose education had been foreign. A well-known instance in Manila was the architect Roxas, father of the present Alcalde of Manila, who learned his profession in England and was almost the only notable builder in Manila during his lifetime.
Paciano Rizal, José’s elder brother, had retired from Page 95Manila on the death of Doctor Burgos and devoted himself to farming; in some ways, perhaps, his career suggested the character of Tasio, the philosopher of “Noli Me Tangere.” He was careful to see that his younger brother was familiar with the liberal literature with which he had become acquainted through Doctor Burgos.
The first foreign book read by Rizal, in a Spanish translation, was Dumas’s great novel, “The Count of Monte Cristo,” and the story of the wrongs suffered by the prisoner of the Château d’If recalled the injustice done his mother. Then came the book which had greatest influence upon the young man’s career; this was a Spanish translation of Jagor’s “Travels in the Philippines,” the observations of a German naturalist who had visited the Islands some fifteen years before. This latter book, among other comments, suggested that it was the fate of the North American republic to develop and bring to their highest prosperity the lands which Spain had conquered and Christianized with sword and cross. Sooner or later, this German writer believed, the Philippine Islands could no more escape this American influence than had the countries on the mainland, and expressed the hope that one day the Philippines would succumb to the same influence; he felt, however, that it was desirable first for the Islanders to become better able to meet the strong competition of the vigorous young people of the New World, for under Spain the Philippines had dreamed away its past.
The exact title of the book is “Travels | in the | Philippines. | By F. Jagor. | With numerous illustrations and a Map | London: | Chapman and Hall, 193, Piccadilly. | 1875.” The title of the Spanish translation reads, “Viajes | por | Filipinas | de F. Jagor | Traducidos del Alemán | por S. Vidal y Soler | Ingeniero de Montes | Edición illustrada con numerosos grabados | Madrid: Imprenta, Estereopidea y Galvanoplastia de Ariban y Ca. Page 96| (Sucesores de Rivadencyra) | Impresores de Camara de S. M. | Calle del Duque de Osuna, núm 3. 1875,” The following extract from the book will show how marvelously the author anticipated events that have now become history:
“With the altered condition of things, however, all this has disappeared. The colony can no longer be kept secluded from the world. Every facility afforded for commercial intercourse is a blow to the old system, and a great step made in the direction of broad and liberal reforms. The more foreign capital and foreign ideas and customs are introduced, increasing the prosperity, enlightenment, and self-esteem of the population, the more impatiently will the existing evils be endured.
England can and does open her possessions unconcernedly to the world. The British colonies are united to the mother country by the bond of mutual advantage, viz., the produce of raw material by means of English capital, and the exchange of the same for English manufactures. The wealth of England is so great, the organization of her commerce with the world so complete, that nearly all the foreigners even in the British possessions are for the most part agents for English business houses, which would scarcely be affected, at least to any marked extent, by a political dismemberment. It is entirely different with Spain, which possesses the colony as an inherited property, and without the power of turning it to any useful account.
Government monopolies rigorously maintained, insolent disregard and neglect of the half-castes and powerful creoles, and the example of the United States, were the chief reasons of the downfall of the American possessions. The same causes threaten ruin to the Philippines; but of the monopolies I have said enough.
Half-castes and creoles, it is true are not, as they formerly were in America, excluded from all orificial appointments; but they feel deeply hurt and injured through the crowds of place-hunters which the frequent changes of Ministers send to Manilla. The influence, also, of the American element is at least visible on the horizon, and will be more noticeable when the relations increase between Page 97the two countries. At present they are very slender. The trade in the meantime follows in its old channels to England and to the Atlantic ports of the United States. Nevertheless, whoever desires to form an opinion upon the future history of the Philippines, must not consider simply their relations to Spain, but must have regard to the prodigious changes which a few decades produce on either side of our planet.
For the first time in the history of the world the mighty powers on both sides of the ocean have commenced to enter upon a direct intercourse with one another—Russia, which alone is larger than any two other parts of the earth; China, which contains within its own boundaries a third of the population of the world; and America, with ground under cultivation nearly sufficient to feed treble the total population of the earth. Russia’s further rôle in the Pacific Ocean is not to be estimated at present.
The trade between the two other great powers will therefore be presumably all the heavier, as the rectification of the pressing need of human labour on the one side, and of the corresponding overplus on the other, will fall to them.
“The world of the ancients was confined to the shores of the Mediterranean; and the Atlantic and Indian Oceans sufficed at one time for our traffic. When first the shores of the Pacific re-echoed with the sounds of active commerce, the trade of the world and the history of the world may be really said to have begun. A start in that direction has been made; whereas not so very long ago the immense ocean was one wide waste of waters, traversed from both points only once a year. From 1603 to 1769 scarcely a ship had ever visited California, that wonderful country which, twenty-five years ago, with the exception of a few places on the coast, was an unknown wilderness, but which is now covered with flourishing and prosperous towns and cities, divided from sea to sea by a railway, and its capital already ranking the third of the seaports of the Union; even at this early stage of its existence a central point of the world’s commerce, and apparently destined, by the proposed junction of the great oceans, to play a most important part in the future.
In proportion as the navigation of the west coast of America extends the influence of the American element over the South Page 98Sea, the captivating, magic power which the great republic exercises over the Spanish colonies1 will not fail to make itself felt also in the Philippines. The Americans are evidently destined to bring to a full development the germs originated by the Spaniards. As conquerors of modern times, they pursue their road to victory with the assistance of the pioneer’s axe and plough, representing an age of peace and commercial prosperity in contrast to that bygone and chivalrous age whose champions were upheld by the cross and protected by the sword.
A considerable portion of Spanish America already belongs to the United States, and has since attained an importance which could not possibly have been anticipated either under the Spanish Government or during the anarchy which followed. With regard to permanence, the Spanish system cannot for a moment be compared with that of America. While each of the colonies, in order to favour a privileged class by immediate gains, exhausted still more the already enfeebled population of the metropolis by the withdrawal of the best of its ability, America, on the contrary, has attracted to itself from all countries the most energetic element, which, once on its soil and, freed from all fetters, restlessly progressing, has extended its power and influence still further and further. The Philippines will escape the action of the two great neighbouring powers all the less for the fact that neither they nor their metropolis find their condition of a stable and well-balanced nature.
It seems to be desirable for the natives that the above-mentioned views should not speedily become accomplished facts, because their education and training hitherto have not been of a nature to prepare them successfully to compete with either of the other two energetic, creative, and progressive nations. They have, in truth, dreamed away their best days.”
Page 99This prophecy of Jagor’s made a deep impression upon Rizal and seems to furnish the explanation of his life work. Henceforth it was his ambition to arouse his countrymen to prepare themselves for a freer state. He dedicated himself to the work which Doctor Jagor had indicated as necessary. It seems beyond question that Doctor Rizal, as early as 1876, believed that America would sometime come to the Philippines, and wished to prepare his countrymen for the changed conditions that would then have to be met. Many little incidents in his later life confirm this view: his eagerness to buy expensive books on the United States, such as his early purchase in Barcelona of two different “Lives of the Presidents of the United States”; his study of the country in his travel across it from San Francisco to New York; the reference in “The Philippines in a Hundred Years”; and the studies of the English Revolution and other Anglo-Saxon influences which culminated in the foundation of the United States of America.

The Books that remain from Rizal’s library.
|
Rizal’s carving of the Sacred Heart. |
Besides the interest he took in clay modeling, to which reference has already been made, Rizal was expert in carving. When first in the Ateneo he had carved an image Page 100of the Virgin of such grace and beauty that one of the Fathers asked him to try an image of the Sacred Heart. Rizal complied, and produced the carving that played so important a part in his future life. The Jesuit Father had intended to take the image with him to Spain, but in some way it was left behind and the schoolboys put it up on the door of their dormitory. There it remained for nearly twenty years, constantly reminding the many lads who passed in and out of the one who teachers and pupils alike agreed was the greatest of all their number, for Rizal during these years was the schoolboy hero of the Ateneo, and from the Ateneo came the men who were most largely concerned in making the New Philippines. The image itself is of batikulin, an easily carved wood, and shows considerable skill when one remembers that an ordinary pocketknife was the simple instrument used in its manufacture. It was recalled to Rizal’s memory when he visited the Ateneo upon his first return from Spain and was forbidden the house by the Jesuits because of his alleged apostasy, and Page 101again in the chapel of Fort Santiago, where it played an important part in what was called his conversion.
|
Bust of Father Guerrico, S. J., modeled from memory by Rizal. Now in the Ateneo, Manila. |
The proficiency he attained in the art of clay modeling is evidenced by many of the examples illustrated in this volume. They not only indicate an astonishing versatility, but they reveal his very characteristic method of working—a characteristic based on his constant desire to adapt the best things he found abroad to the conditions of his own country. The same characteristic appears also in most of his literary work, and in it there is no servile imitation; it is careful and studied selection, adaptation and combination. For example, the composition of a steel engraving in a French art journal suggested his model in clay of a Philippine wild boar; the head of the subject in a painting in the Luxembourg Gallery and the rest of a figure in an engraving in a newspaper are combined in a statuette he modeled in Brussels and sent, in May, 1890, to Valentina Ventura in place of a letter; a clipping from a newspaper cut is also adapted for his model of “The Vengeance of the Harem”; and as evidence of his facility of expressing himself in this medium, his clay modeling of a Dapitan woman may be cited. One day while in exile he saw a native woman clearing up the street in front of her home preparatory to a festival; the movements and the attitudes of the figure were so thoroughly typical and so impressed themselves on his mind that he worked out this statuette from memory. Page 102

A composite statuette by Rizal: the head from a painting in the Luxembourg (shown in upper right-hand corner), the rest from an engraving.
In a literary way Rizal’s first pretentious effort was a melodrama in one act and in verse, entitled “Junta al Pasig” (Beside the Pasig), a play in honor of the Virgin, which was given in the Ateneo to the great edification of a considerable audience, who were enthusiastic in their praise and hearty in their applause, but the young author neither saw the play nor paid any attention to the manner of its reception, for he was downstairs, intent on his own diversions and heedless of what was going on above.

Clay model of a Dapitan woman, from life, by Rizal.
Thursday was the school holiday in those days, and Page 104Rizal usually spent the time at the Convent of La Concordia, where his youngest sister, Soledad, was a boarder. He was a great friend of the little one and a welcome visitor in the Convent; he used to draw pictures for her edification, sometimes teasing her by making her own portrait, to which he gave exaggerated ears to indicate her curiosity. Then he wrote short satirical skits, such as the following, which in English doggerel quite matches its Spanish original:
“The girls of Concordia College
Go dressed in the latest of styles—
Bangs high on their foreheads for knowledge—
But hungry their grins and their smiles!”
Some of these girls made an impression upon José, and one of his diary entries of this time tells of his rude awakening when a girl, some years his elder, who had laughingly accepted his boyish adoration, informed him that she was to marry a relative of his, and he speaks of the heart-pang with which he watched the carromata that carried her from his sight to her wedding.
José was a great reader, and the newspapers were giving much attention to the World’s Fair in Philadelphia which commemorated the first centennial of American independence, and published numerous cuts illustrating various interesting phases of American life. Possibly as a reaction from the former disparagement of things American, the sentiment in the Philippines was then very friendly. There was one long account of the presentation of a Spanish banner to a Spanish commission in Philadelphia, and the newspapers, in speaking of the wonderful progress which the United States had made, recalled the early Spanish alliance and referred to the fact that, had it not been for the discoveries of the Spaniards, their new land would not have been known to Europe.
Page 105Rizal during his last two years in the Ateneo was a boarder. Throughout his entire course he had been the winner of most of the prizes. Upon receiving his Bachelor of Arts diploma he entered the University of Santo Tomás; in the first year he studied the course in philosophy and in the second year began to specialize in medicine.
|
A sketch of himself by Rizal, in the training class. |
The Ateneo course of study was a good deal like that of our present high school, though not so thorough nor so advanced. Still, the method of instruction which has made Jesuit education notable in all parts of the world carried on the good work which the mother’s training had begun. The system required the explanation of the morrow’s lesson, questioning on the lesson of the day and a review of the previous day’s work. This, with the attention given to the classics, developed and quickened faculties which gave Rizal a remarkable power of assimilating knowledge of all kinds for future use.
The story is told that Rizal was undecided as to his career, and wrote to the rector of the Ateneo for advice; but the Jesuit was then in the interior of Mindanao, and by the time the answer, suggesting that he should devote himself to agriculture, was received, he had already made his choice. However, Rizal did continue the study of agriculture, besides specializing in medicine, carrying on double work as he took the course in the Ateneo which led to the degree of land surveyor and agricultural expert. This work was completed before he had reached the age Page 106fixed by law, so that he could not then receive his diploma, which was not delivered to him until he had attained the age of twenty-one years.

Rizal’s sister Saturnina. Painted in oil by José Rizal while in Santo Tomás University.
In the “Life” of Rizal published in Barcelona after his death a brilliant picture is painted of how Rizal might have followed the advice of the rector of the Ateneo, and have lived a long, useful and honorable life as a farmer and gobernadorcillo of his home town, respected by the Spaniards, looked up to by his countrymen and filling an humble but safe lot in life. Today one can hardly feel Page 107that such a career would have been suited to the man or regret that events took the course they did.
Poetry was highly esteemed in the Ateneo, and Rizal frequently made essays in verse, often carrying his compositions to Kalamba for his mother’s criticisms and suggestions. The writings of the Spanish poet Zorilla were making a deep impression upon him at this time, and while his schoolmates seemed to have been more interested in their warlike features, José appears to have gained from them an understanding of how Zorilla sought to restore the Spanish people to their former dignity, rousing their pride through recalling the heroic events in their past history. Some of the passages in the melodrama, “Junta al Pasig,” already described, were evidently influenced by his study of Zorilla; the fierce denunciation of Spain which is there put in the mouth of Satan expresses, no doubt, the real sentiments of Rizal.
In 1877 a society known as the Liceo Literario-Artistica (Lyceum of Art and Literature) offered a prize for the best poem by a native. The winner was Rizal with the following verses, “Al Juventud Filipino” (To the Philippine Youth). The prize was a silver pen, feather-shaped and with a gold ribbon running through it.
To the Philippine Youth
Theme: “Growth”
(Translation by Charles Derbyshire)
Hold high the brow serene,
O youth, where now you stand;
Let the bright sheen
Of your grace be seen,
Fair hope of my fatherland!
Come now, thou genius grand,
And bring down inspiration;
With thy mighty hand,
Swifter than the wind’s volation,
Raise the eager mind to higher station.
Come down with pleasing light
Of art and science to the fight,
O youth, and there untie
The chains that heavy lie,
Your spirit free to blight.
See how in flaming zone
Amid the shadows thrown,
The Spaniard’s holy hand
A crown’s resplendent band
Proffers to this Indian land.
Thou, who now wouldst rise
On wings of rich emprise,
Seeking from Olympian skies
Songs of sweetest strain,
Softer than ambrosial rain;
Thou, whose voice divine
Rivals Philomel’s refrain,
And with varied line
Through the night benign
Frees mortality from pain;
Thou, who by sharp strife
Wakest thy mind to life;
And the memory bright
Of thy genius’ light
Makest immortal in its strength;
And thou, in accents clear
of Phoebus, to Apells dear;
Or by the brush’s magic art
Takest from nature’s store a part,
To fix it on the simple canvas’ length;
Go forth, and then the sacred fire
Of thy genius to the laurel may aspire;
To spread around the fame,
And in victory acclaim,
Through wider spheres the human name.
Day, O happy day,
Fair Filipinas, for thy land!
So bless the Power today
That places in thy way
This favor and this fortune grand.
The next competition at the Liceo was in honor of the fourth centennial of the death of Cervantes; it was open to both Filipinos and Spaniards, and there was a dispute as to the winner of the prize. It is hard to figure out just what really happened; the newspapers speak of Rizal as winning the first prize, but his certificate says second, and there seems to have been some sort of compromise by which a Spaniard who was second was put at the head. Newspapers, of course, were then closely censored, but the liberal La Oceania contains a number of veiled allusions to medical poets, suggesting that for the good of humanity they should not be permitted to waste their time in verse-making. One reference quotes the title of Rizal’s first poem in saying that it was giving a word of advice “To the Philippine Youth,” and there are other indications that for some considerable time the outcome of this contest was a very live topic in the city of Manila.
Page 110Rizal’s poem was an allegory, “The Council of the Gods”—“El consejo de los Dioses.” It was an exceedingly artistic appreciation of the chief figure in Spanish literature. The rector of the Ateneo had assisted his former student by securing for him needed books, and though Rizal was at that time a student in Santo Tomás, the rivalries were such that he was still ranked with the pupils of the Jesuits and his success was a corresponding source of elation to the Ateneo pupils and alumni. Some people have stated that Father Evaristo Arias, a notably brilliant writer of the Dominicans, was a competitor, a version I once published, but investigation shows that this was a mistake. However, sentiment in the University against Rizal grew, until matters became so unpleasant that he felt it time to follow the advice of Father Burgos and continue his education outside of the Islands.
Just before this incident Rizal had been the victim of a brutal assault in Kalamba; one night when he was passing the barracks of the Civil Guard he noted in the darkness a large body, but did not recognize who it was, and passed without any attention to it. It turned out that the large body was a lieutenant of the Civil Guard, and, without warning or word of any kind, he drew his sword and wounded Rizal in the back. Rizal complained of this outrage to the authorities and tried several times, without success, to see the Governor-General. Finally he had to recognize that there was no redress for him. By May of 1882 Rizal had made up his mind to set sail for Europe, and his brother, Paciano, equipped him with seven hundred pesos for the journey, while his sister, Saturnina, intrusted to him a valuable diamond ring which might prove a resource in time of emergency.
José had gone to Kalamba to attend a festival there, when Mr. Hidalgo, from Manila, notified him that his boat was ready to sail. The telegram, asking his immediate Page 111return to the city, was couched in the form of advice of the condition of a patient, and the name of the steamer, Salvadora, by a play on words, was used in the sense of “May save her life.” Rizal had previously requested of Mr. Ramirez, of the Puerta del Sol store, letters of introduction to an Englishman, formerly in the Philippines, who was then living in Paris. He said nothing more of his intentions, but on his last night in the city, with his younger sister as companion, he drove all through the walled city and its suburbs, changing horses twice in the five hours of his farewell. The next morning he embarked on the steamer, and there yet remains the sketch which he made of his last view of the city, showing its waterfront as it appeared from the departing steamer. To leave town it was necessary to have a passport; his was in the name of José Mercado, and had been secured by a distant relative of his who lived in the Santa Cruz district.

Rizal’s parting view of Manila. A pencil sketch by himself.
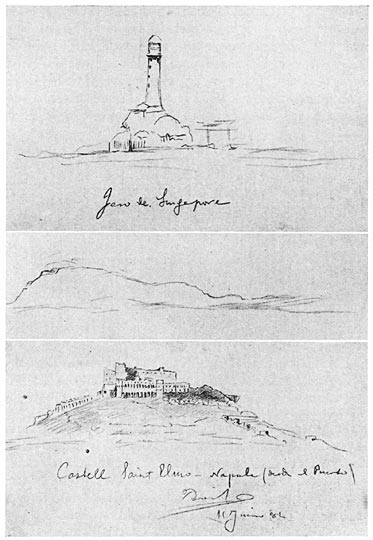
Sketches
1. Singapore Lighthouse. 2. Along the Suez Canal. 3. Castle of St. Elmo, Naples. (From Rizal’s Sketch-book)
After five days’ journey the little steamer reached the Page 112Page 113English colony of Singapore. There Rizal saw a modern city for the first time. He was intensely interested in the improvements. Especially did the assured position of the natives, confident in their rights and not fearful of the authorities, arouse his admiration. Great was the contrast between the fear of their rulers shown by the Filipinos and the confidence which the natives of Singapore seemed to have in their government.

Studies of passengers on the French mail steamer.
(From Rizal’s sketch-book.)
At Singapore, Rizal transferred to a French mail Page 114Page 115Steamer and seems to have had an interesting time making himself understood on board. He had studied some French in his Ateneo course, writing an ode which gained honors, but when he attempted to speak the language he was not successful in making Frenchmen understand him. So he resorted to a mixed system of his own, sometimes using Latin words and making the changes which regularly would have occurred, and when words failed, making signs, and in extreme cases drawing pictures of what he wanted. This versatility with the pencil, for many of his offhand sketches had humorous touches that almost carried them into the cartoon class, interested officers and passengers, so that the young student had the freedom of the ship and a voyage far from tedious.

Aden—May 28, 1882. (From Rizal’s Sketch-book.)
The passage of the Suez Canal, a glimpse of Egypt, Aden, where East and West meet, and the Italian city of Naples, with its historic castle, were the features of the trip which most impressed him. Page 116
1 I take the liberty, here, of citing an instance of this. In 1861, when I found myself on the West Coast of Mexico, a dozen backwoods families determined upon settling in Sonora (forming an oasis in the desert); a plan which was frustrated by the invasion at that time of the European powers. Many native farmers awaited the arrival of these immigrants in order to take them under their protection. The value of land in consequence of the announcement of the project rose very considerably.
Chapter VI
The Period of Preparation
Rizal disembarked at Marseilles, saw a little of that famous port, and then went by rail to Barcelona, crossing the Pyrenees, the desolate ruggedness of which contrasted with the picturesque luxuriance of his tropical home, and remained a day at the frontier town of Port-Bou. The customary Spanish disregard of tourists compared very unfavorably with the courteous attention which he had remarked on his arrival at Marseilles, for the custom house officers on the Spanish frontier rather reminded him of the class of employes found in Manila.
At Barcelona he met many who had been his schoolmates in the Ateneo and others to whom he was known by name. It was the custom of the Filipino students there to hold reunions every other Sunday at the café, for their limited resources did not permit the daily visits which were the Spanish custom. In honor of the new arrival a special gathering occurred in a favorite café in Plaza de Catalonia. The characteristics of the Spaniards and the features of Barcelona were all described for Rizal’s benefit, and he had to answer a host of questions about the changes which had occurred in Manila. Most of his answers were to the effect that old defects had not yet been remedied nor incompetent officials supplanted, and he gave a rather hopeless view of the future of their country. Somewhat in this gloomy mood, he wrote home for a newly established Tagalog newspaper of Manila, his views of “Love of country,” an article not so optimistic as most of his later writings.
In Barcelona he remained but a short time, long enough, however, to see the historic sights around that city, which was established by Hannibal, had numbered Page 117many noted Romans among its residents, and in later days was the scene of the return of Columbus from his voyages in the New World, bringing with him samples of Redskins, birds and other novel products of the unknown country. Then there were the magnificent boulevards, the handsome dwellings, the interest which the citizens took in adorning their city and the pride in the results, and above all, the disgust at all things Spanish and the loyalty to Catalonia, rather than to the “mother-fatherland.”
The Catalan was the most progressive type in Spain, but he had no love for his compatriots, was ever complaining of their “mañana” habits and of the evils that were bound to exist in a country where Church and State were so inextricably intermingled. Many Catalans were avowedly republicans. Signs might be seen on the outside of buildings telling of the location of republican clubs, unpopular officials were hooted in the streets, the newspapers were intemperate in their criticism of the government, and a campaign was carried on openly which aimed at changing from a monarchy to a democracy, without any apparent molestation from the authorities. All these things impressed the lad who had seen in his own country the most respectfully worded complaints of unquestionable abuses treated as treason, bringing not merely punishment, but opprobrium as well.
He, himself, in order to obtain a better education, had had to leave his country stealthily like a fugitive from justice, and his family, to save themselves from persecution, were compelled to profess ignorance of his plans and movements. His name was entered in Santo Tomás at the opening of the new term, with the fees paid, and Paciano had gone to Manila pretending to be looking for this brother whom he had assisted out of the country.
Early in the fall Rizal removed to Madrid and entered Page 118the Central University there. His short residence in Barcelona was possibly for the purpose of correcting the irregularity in his passport, for in that town it would be easier to obtain a cedula, and with this his way in the national University would be made smoother. He enrolled in two courses, medicine, and literature and philosophy; besides these he studied sculpture, drawing and art in San Carlos, and took private lessons in languages from Mr. Hughes, a well-known instructor of the city. With all these labors it is not strange that he did not mingle largely in social life, and lack of funds and want of clothes, which have been suggested as reasons for this, seem hardly adequate. José had left Manila with some seven hundred pesos and a diamond ring. Besides, he received funds from his father monthly, which were sent through his cousin, Antonio Rivera, of Manila, for fear that the landlords might revenge themselves upon their tenant for the slight which his son had cast upon their university in deserting it for a Peninsular institution. It was no easy task in those days for a lad from the provinces to get out of the Islands for study abroad.
Rizal frequently attended the theater, choosing especially the higher class dramas, occasionally went to a masked ball, played the lotteries in small amounts but regularly, and for the rest devoted most of his money to the purchase of books. The greater part of these were second-hand, but he bought several standard works in good editions, many with bindings de luxe. Among the books first purchased figure a Spanish translation of the “Lives of the Presidents of the United States,” from Washington to Johnson, morocco bound, gilt-edged, and illustrated with steel engravings—certainly an expensive book; a “History of the English Revolution;” a comparison of the Romans and the Teutons, and several other books which indicated interest in the freer system Page 119of the Anglo-Saxons. Later, another “History of the Presidents,” to Cleveland, was added to his library.
The following lines, said to be addressed to his mother, were written about this time, evidently during an attack of homesickness:



