Analysis Of Variance
Analysis of Variance:
Analysis of variance basically is an arithmetical method by which we split up the total variability into component variations ascribable to different sources of causes. In the words of Yule and Kendall, The analysis of variance is essentially a procedure for testing the difference between different groups of data for homogeneity. While defining analysis of variance, Ronal A. Fisher wrote, The separation of the variance ascribable to one group of causes from the variance ascribable to other groups. In simple words, Analysis of Variance is a statistical technique, with help of which total variation, is partitioned into variation caused by each set of independent factors and homogeneity of several means is tested.
Components of Total Variability:
In general (say one way classification) total variability is partitioned into two parts that is:
Total Variability = Variability between samples Variability within samples.
Or
Total Variation = Variation between samples Variation within samples.
Assumptions of Analysis of Variance:
The analysis of variance is based on certain assumptions as given below :
1. Normality of the Distribution : The population for each sample must be normally distributed with mean μ and unknown variance σ 2.
2. Independence of Samples : All the sample observations must be selected randomly. The total variation of the various sources of variation should be additive.
3. Additivity : The total variation of the various sources of variation should be additive.
4. Equal variances (but unknown) : The populations from which the n samples say are drawn have means μ1, μ2, ..., μn and unknown variance σ 2 1 = σ 2 2 = ...... = σ 2 n = σ 2.
5. The error components are independent and have mean 0 and variance σ 2.
The tests of significance performed in the analysis of variance are meaningful under its assumptions.
Analysis of Variance Table:
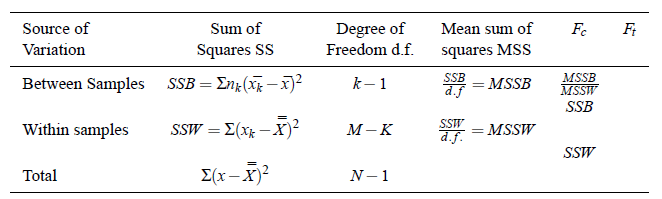
Remark: There are three methods, to calculate mean and variances :
(i) Direct Method
(ii) Indirect Method
(iii) Step deviation Method or Coding Method (change of origin or / and scale)