Ac-coupled Amplifiers
AC-Coupled Amplifiers
The dc component of a signal can be blocked off by connecting the signal through a capacitor (Note that the impedance of a capacitor is 1/(jwC) and hence, at zero frequency there will be an infinite impedance).
If the input lead of a device has a series capacitor, we say that the input is ac-coupled and if the output lead has a series capacitor, then the output is ac-coupled.
Typically, an ac-coupled amplifier has a series capacitor both at the input lead and the output lead. Hence, its frequency response function will have a high pass characteristic; in particular, the dc components will be filtered out. Errors due to bias currents and offset signals are negligible for an ac-coupled amplifier.
Furthermore, in an ac-coupled amplifier, stability problems are not very serious.
Ground Loop Noise
In instruments that handle low-level signals (e.g., sensors such as accelerometers; signal conditioning circuitry such as strain gage bridges; and sophisticated and delicate electronic components such as computer disk drives and automobile control modules) electrical noise can cause excessive error unless proper corrective actions are taken.
One form of noise is caused by fluctuating magnetic fields due to nearby ac power lines or electric machinery.
This is commonly known as electromagnetic interference (EMI). This problem can be avoided by removing the source of EMI so that fluctuating external magnetic fields and currents are not present near the affected instrument.
Another solution would be to use fiber optic (optically coupled) signal transmission so that there is no noise conduction along with the transmitted signal from the source to the subject instrument.
In the case of hard-wired transmission, if the two signal leads (positive and negative or hot and neutral) are twisted or if shielded cables are used, the induced noise voltages become equal in the two leads, which cancel each other.
Proper grounding practices are important to mitigate unnecessary electrical noise problems and more importantly, to avoid electrical safety hazards.
A standard single-phase ac outlet (120 V, 60 Hz) has three terminals, one carrying power (hot), the second being neutral, and the third connected to earth ground (which is maintained at zero potential rather uniformly from point to point in the power network).
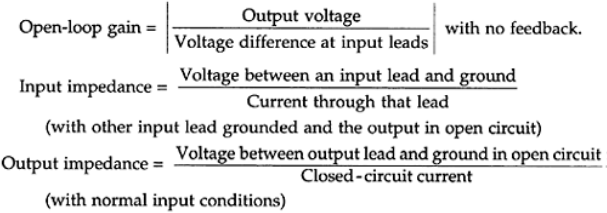
Bandwidth=frequency range in which the frequency response is flat (gain is constant).
1. Gain bandwidth product (GBP) =Open loop gain×Bandwidth at that gain
2. Input bias current=average (dc) current through one input lead
3. Input offset current=difference in the two input bias currents
4. Differential input voltage=voltage at one input lead with the other grounded when the output voltage is zero.
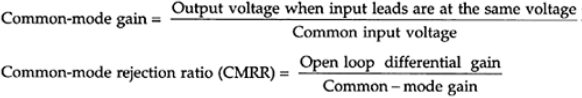
Slew rate=rate of change of output of a unity-gain op-amp, for a step input plug of an instrument should have three prongs.