Thermal Elements
Thermal Elements
Here the across variable is temperature (T) and the through variable is the heat transfer rate (Q). The thermal capacitor is an A-type element. There is no T-type element in a thermal system. The reason is clear. There is only one type of energy (thermal energy) in a thermal system, whereas there are two types of energy in mechanical and electrical systems.
Thermal Capacitor
Consider a thermal volume u of fluid with, density r, and specific heat c. Then, for a net heat transfer rate Q into the control volume we have
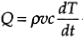
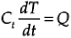
Where, Ct=rcis the thermal capacitance of the control volume
There are three basic processes of heat transfer:
1. Conduction
2. Convection
3. Radiation
There is a thermal resistance associated with each process, given by its constitutive relation, as indicated below.

Where
k=conductivity
A=area of cross section of the heat conduction element
Dx=length of heat conduction that has a temperature drop of T
The conductive resistance
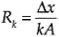
Convection: Q=hcAT
Where
hc=convection heat transfer coefficient
A=area of heat convection surface with a temperature drop of T
The conductive resistance
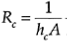

where
s=Stefan-Boltzmann constant
FE=effective emissivity of the radiation source (of temperature T1)
FA=shape factor of the radiation receiver (of temperature T2)
A=effective surface area of the receiver
This corresponds to a nonlinear thermal resistor.