Michelson- Morley Experiment
Michelson- Morley experiment: Michelson-Morley set up a sensitive optical set up for measuring the velocity of light with respect to relative velocity of ether medium, which flows past opposite to the direction of earth movement. The details of the experimental set up is as follows:
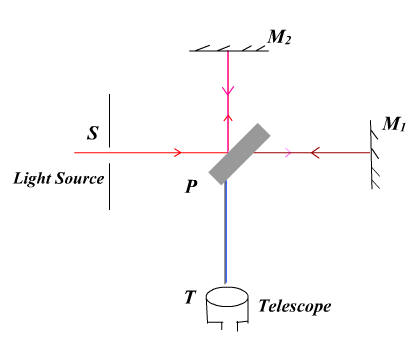
Light beam from the source 'S' is incident at ![]() on a beam splitter, which is a semi silvered glass plate P. The plate splits the beam into two coherent beams and out of them one is transmitted through P and other one is reflected at P. The transmitted rays strike the mirror
on a beam splitter, which is a semi silvered glass plate P. The plate splits the beam into two coherent beams and out of them one is transmitted through P and other one is reflected at P. The transmitted rays strike the mirror ![]() and from there it is reflected back to plate P. The reflected beam at P strike the mirror
and from there it is reflected back to plate P. The reflected beam at P strike the mirror ![]() and it is also reflected back to plate P.
and it is also reflected back to plate P.
The returned beam from ![]() is partially reflected by the plate P to reach the telescope. The returned beam from
is partially reflected by the plate P to reach the telescope. The returned beam from ![]() is partially transmitted by the plate P to reach the telescope T. The superposition of these two rays produce interference pattern, which are seen through the telescope T. The in-phase signals interfere constructively to give bright band and the out of phase signals interfere destructively to give dark band.
is partially transmitted by the plate P to reach the telescope T. The superposition of these two rays produce interference pattern, which are seen through the telescope T. The in-phase signals interfere constructively to give bright band and the out of phase signals interfere destructively to give dark band.
The two rays travel different optical paths, ![]() = P
= P![]() and
and ![]() = P
= P![]() . If a bright fringe is seen on the cross wire of T, the path difference between two rays must be an integral multiple of
. If a bright fringe is seen on the cross wire of T, the path difference between two rays must be an integral multiple of ![]() , i.e., we have,
, i.e., we have,
2![]() - 2
- 2![]() = m
= m![]() ...................... ( 1 )
...................... ( 1 )
where m is an integer. The factor 2 is to account for the to and fro paths of rays between plate P and Mirrors.
Now suppose that entire apparatus is kept on a sturdy platform on the surface of earth such that the path P![]() is parallel to the direction of motion of earth through ether; that is the apparatus is moving with at speed
is parallel to the direction of motion of earth through ether; that is the apparatus is moving with at speed ![]() in direction P
in direction P![]() relative to ether, where
relative to ether, where ![]() is the velocity of earth. The time taken by the first ray from P to
is the velocity of earth. The time taken by the first ray from P to ![]() and back is,
and back is,
![]()
 ........................... ( 2 )
........................... ( 2 )
In order to calculate the time taken by the second beam to reach ![]() and back to plate P, we have to take the motion of
and back to plate P, we have to take the motion of ![]() along the direction of P
along the direction of P![]() .
.
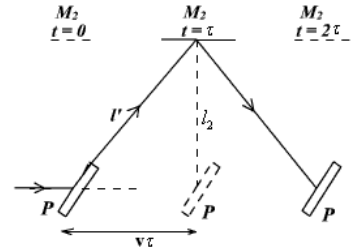
At t = 0, the light beam is reflected by the plate P and it reaches the mirror ![]() at t =
at t = ![]() . The plate and mirror assembly traveled a horizontal distance of
. The plate and mirror assembly traveled a horizontal distance of ![]()
![]() during this time t . At t =2
during this time t . At t =2![]() , the light returns back to plate P.
, the light returns back to plate P.