Optical Fiber Communications
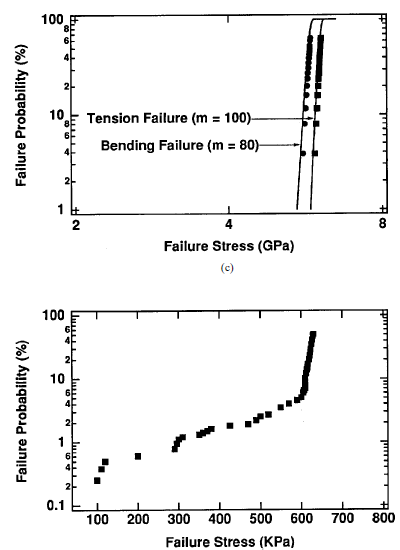
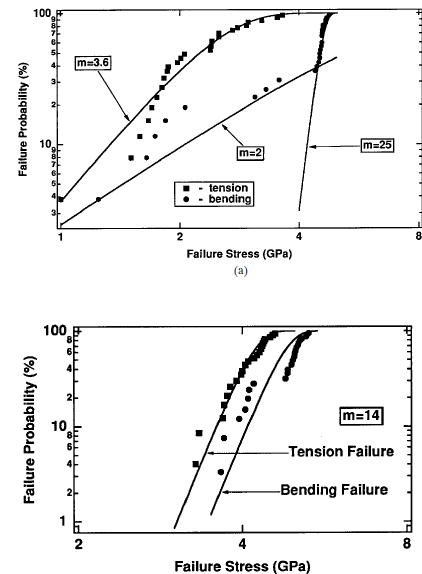 fig..(1)A series of Weibull plots comparing bending and tensile strength for
fig..(1)A series of Weibull plots comparing bending and tensile strength for
( a ) low , ( b ) intermediate , and ( c ) high values of the Weibull exponent m ; ( d ) shows a typical mean time to failure plot . Actual fibers will often exhibit slope discontinuities , indicating a change in the dominant failure mechanism . (Data Courtesy of Corning , Inc . )
approximately flat and at a fixed ratio (expressed in dB) to the laser power . Figure 4 shows a typical plot of the relative intensity noise of a source . The specification of RIN as a flat noise source is valid only at frequencies much less than the relaxation oscillation frequency and in situations where reflections are small . The relative intensity noise is af fected rather dramatically by the environment of the
diode laser . A rather weak reflection back into the laser will both increase the magnitude of the relative intensity noise and modify its spectrum . As the reflection increases , it can produce self-pulsations and chaos in the output of the laser , rendering it useless for communications applications . 3 7 Thus , the laser cannot be thought of as an isolated component in the communications system . Just as RF and microwave systems require impedance matching for good performance , an optical communications system must minimize reflections . This is relatively easily accomplished for a long distance telecommunications link which makes use of low-reflection fusion splices . However , in a short
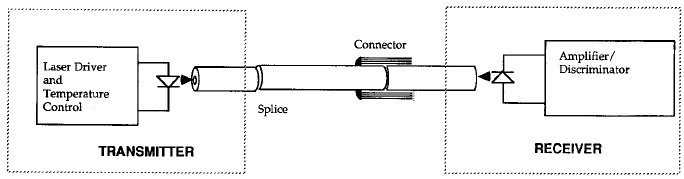
link-network environment which must be modular , a small number of connectors can cause severe problems unless those connectors are designed to minimize reflections . It is now widely accepted that optical fiber connectors must be specified both in terms of insertion loss and reflection . A 1 percent reflection from a fiber connector can have far more serious implications for an optical fiber link than a 1 percent loss which is not reflected back to the
laser . Optical isolators are available but only at considerable expense and are not generally considered economically realistic for network environments .