Probability Distribution Terminology
Probability distribution terminology:
1. Variables can bequantitative or qualitative.
2. Quantitative variablesare measured numerically in a discrete or continuous manner, whereas qualitative variablesare measured in a descriptive manner.
3. For example, system throughput is a quantitative variable and product color is a qualitative variable.
4. Variables are also dependent and independent.
5. Simulationinput variables such as number of machines, entities arrival rates, and cycle times are independent variables, whereas model outcomes such as throughput and lead time are dependent variables.
6. Finally, variables are either continuous or discrete. A continuous variable is one for which any value is possible within the limits the variable ranges.
Parameters and Statistics:
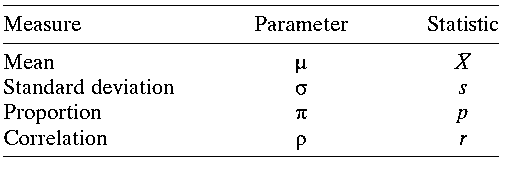
a) The word statisticsis used in several different senses.
b) In the broadest sense, statistics refers to a range of techniques and procedures for analyzing data, interpreting data, displaying data, and making decisions based on data.
c) The term also refers to the numerical quantity calculated from a sample of size n. Such statistics are used for parameter estimation.
d) In analyzing simulation outputs, it is also essential to distinguish between statistics and parameters. Whereas statistics are measured from data samples of limited size (n), a parameter is a numerical quantity that measures some aspect of the data population.
e) Population consists of an entire set of objects, observations, or scores that have something in common.
f) The distribution of a population can be described by several parameters, such as the mean and the standard deviation. Estimates of these parameters taken from a sample are called statistics.
g) A sample is, therefore, a subset of a population. Since it is usually impractical to test every member of a population, a sample from the population is typically the best approach available.
h) For example, the average of system throughput in 100 hours of run time is a statistic, whereas the generic throughput mean over the plant history is a parameter.
i) Population parameters are rarely known and are usually estimated by statistics computed using samples.