←
Six Sigma
Process Capability Indices
Fuzzy PCA and PCIs:
- As stated before, though FLs’ broad range of application has also affected studies on PCA and PCIs, the fuzzy based perspective on these areas are relatively new. The first spectacular fuzzy PCI studies; to our knowledge, can be traced back to the fuzzy quality and probability study of Yongting (1996); in which, a fuzzy Cpk was defined to determine the fuzzy quality.
- Later Lee et al. (1999) declared a fuzzy based model to maximize PCI via determining upper and lower bounds of PCIs using membership functions. In 2001, Lee proposed an estimation approach for fuzzy Cpk using fuzzy observations comprised of fuzzy numbers.
-
One of the worth mentioning fuzzy based study about process capability evaluation is made by Chen et al. (2003). Chen and his research colleagues proposed a method to interlink PCI with a fuzzy inference system for “bigger-the-best” type evaluation. In the study, the input for the fuzzy inference is the p value is calculated as follow;
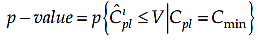
Six Sigma methodology:
Relationship between process capability and Six Sigma:
- The technical elaboration of Six Sigma can be achieved through the use of normal distribution and PCIs.
- Historically, the creators of Six Sigma employed Cp, as it was accepted as a standard quality measure.
- Six Sigma was developed for solving the complexity of products and observing the failure of the products in order to achieve the predictive performances.
- Similar to Six Sigma methodology, in a process capability study, the number of standard deviations between the process mean and the nearest specification limits is given in sigma units.
- The sigma quality level of a process can be used to express its capability that means how well it performs with respect to the specification limits. By the way, in terminology of statistics, sigma represents the variation about the process mean. The application of Six Sigma methodology provides reduction in variance and augmentation in the process capability. As it is mentioned above, a Six Sigma process can be interpreted in terms of process capability, which is associated with process variation by using PCI, such as Cpk.
- Nowadays, most of the manufacturers are required to produce a product with a specified Cpk value. As the market competition is getting tougher and tougher, organizations are under pressure to sustain world class competition so that they need to meet or exceed this specified Cpk value or quality level.
- It should be noticed that Cpk values are related to sigma quality levels. Higher value of Cpk indicates a better process. For instance; a process capability, that is, Cpk of 1.00 is roughly equivalent to three sigma capability. That is, the mean plus and the mean minus three standard deviations should be the points at which the nearest specification limits lie. With three sigma capability or Cpk = 1.00, a process will produce approximately 99.73% good product or 0.27% bad product. This represents an unacceptably high level of poor products.
- On the other hand, nowadays high quality standards dictate reducing variation by four standard deviations between the process mean and the nearest specifications. This corresponds to the value of Cpk = 1.33. At this level, the process will produce approximately 99.9937% good product or 0.0063% bad product. This represents a better figure than the figure of three sigma capability (or Cpk = 1.00), but it is still having high level of poor products.
- Process capability measures have been used to provide number of nonconforming product. As it is mentioned in earlier sections, ppm is used in this regard. At ± 3 sigma level, the probability of producing a product within specification limits is 0.9973. This implies 2700 ppm.
- Therefore, at a six sigma capability level, a process will produce very few defects. This level represents a Cpk value of 2.0 which is more commonly referred to as six sigma capability.