Selection Process Of Six Sigma Projects
Proposal of a model for strategic alignment of Six Sigma Projects : Santos and Martins (2005) propose a framework that expresses the relationship of performance indicators with the Six Sigma program as a reflection of the strategic alignment. The structure is described in nine points:
A. The organization interacts with the environment to define the strategy;
B. Construction of the performance measurement system that is aligned to the strategy;
C. The multiple categories of the performance measurement system direct the actions of the Six Sigma program by aligning the selection of Six Sigma projects;
D. The Six Sigma projects should be aligned with the strategy through its objectives;
E. The results from setting up the Six Sigma projects can promote improved efficiency and effectiveness of the company’s processes;
F. The Six Sigma projects may need a revision of its goals to achieve a greater alignment;
G. The Six Sigma projects have a role as performance drivers through the link they establish with the performance measures that make up the performance measurement system;
H. Customer satisfaction is achieved to the extent that goods and services are improved, and
I. The successful implementation of Six Sigma projects enables an important strategic feedback in order to review the strategic objectives.
This structure demonstrates that selecting the projects has a strong relationship with the company’s indicators and strategic direction; points three and four of this structure, previously listed.
This systematization, however, does not describe in detail the selection process of Six Sigma projects, however, it details the unfolding of the strategy and the importance of its alignment with the Six Sigma projects, through the selection process of Six-Sigma projects.
Quality function deployment:
1. The deployment of the quality functions contributes to the improvement of the process and facilitates the planning of the system design in agreement with the positioning of the company in its competing environment.
2. The crucial importance of QFD is considered in the process of communication that it generates as well as in the decision-making.
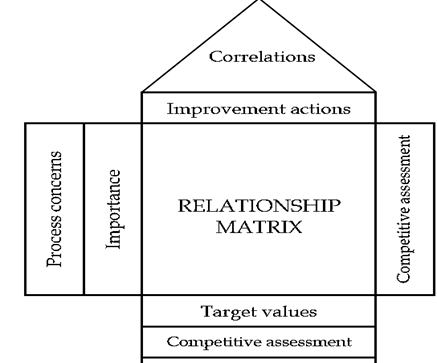
3. The QFD process involves constructing one or more matrices.
4. The first one is called the House of Quality (HoQ). This consists of several sections or sub-matrices joined together in various ways, each of which containing information related to the others.
5. There are nearly as many forms of the HoQ as there have been applications and it is this adaptability to the needs of a particular project or user group, which is one of its strengths.