←
Six Sigma
Statistical Interpretation Of Six-sigma
Statistical interpretation of Six Sigma:
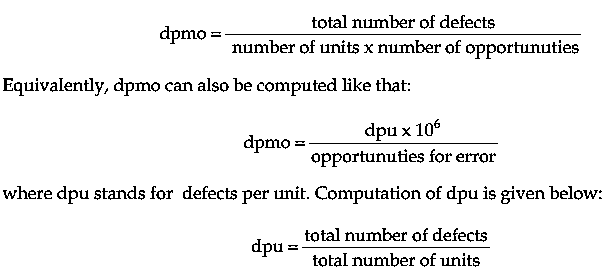
- In Six Sigma process, as its name implies, there are six standard deviations between the process mean and specification limits, when the process is centered. The objective of using Six Sigma approach is to reduce process variation, and thereby defects. The six sigma metric uses dpmo, which is the abbreviation for defects per million opportunities.
- It is essential to be consistent about the definition of the opportunities because by increasing the number of opportunities over time, a process may be artificially improved (Montgomery, 2009). Computation of dpmo is given below:
Six Sigma methodology:
- In order to sustain world-class competition, organizations should attain Six Sigma activities by integrating their knowledge of the process with statistics, engineering and project management (Anbari, 2002).
- Six Sigma is a quality management philosophy as well as a methodology that focuses on reducing variation, eliminating defects and improving the quality of processes, products and services.
- In other words, Six Sigma Methodology is defined as a data-driven, statistics-based approach and a project-driven management that improves processes, products and services of organization by continuously reducing both nonconforming items or mistakes and variation as well as costs in the organization.
- In the literature, Six Sigma has also proven to be a customer-focused and a robust methodology. In practice, organizations should give importance to improve overall performance instead of detecting and counting defects. The application of Six Sigma methodology provides reduction in variance and augmentation in the process capability, and process performance, simultaneously. Significant improvement in process capability and process performance can be achieved after a successful implementation of Six Sigma methodology that is accepted as a rigorous concept of quality control with this feature.
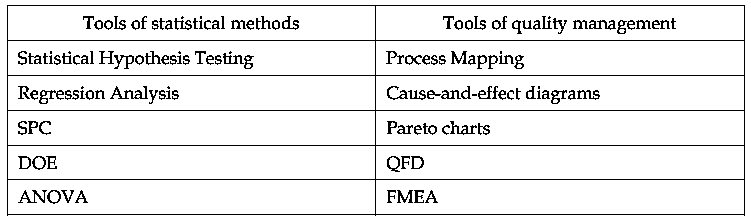
- According to Allen (2006), tools that are used in Six Sigma methodology can be categorized as tools of statistical methods and quality management, which are very useful in identifying and eliminating causes of defects in business processes by examining the inputs, the outputs, and the relationship between the inputs and outputs.