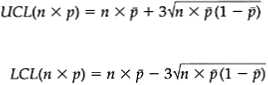Control Charts
Introduction:
Control charts may be used partly to control variation and partly in the identification and control of the causes which give rise to these variations.
The p chart:
For each sample (subgroup) the failure proportion (p) is calculated and charted in the control chart. The failure proportion is calculated as shown below:
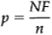
Where:
NF=number of failures in the sample
n=sample size (number inspected in sub group)
Construction of control limits is done as follows:
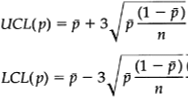
Where: 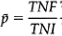
And:
TNF=Total Number of Failures in all the samples inspected
TNI=Total Number Inspected (the sum of all samples).
- For varying sample sizes the control limits vary from sample to sample.
- If varying control limits may give problems to the users then plan for fixed sample sizes.
- For small variations (±20%) using the average sample size is recommended. The benefit of using the average sample size is that the control limits are constant from sample to sample.
The np chart:
For each sample the number of failures (np=the number of non-conforming units) is counted and charted in the control chart. Construction of the control limits is done as follows: