←
Total Quality Management (TQM)
Flow Charts
Introduction:
Making and using flow charts are among the most important actions in bringing process control to both administrative and manufacturing processes. The easiest and best way to understand a process is to draw a picture of it—that’s basically what flow charting is.
DEFINE THE PROCESS:
It is important to define the boundaries of the process, i.e. the first activity which you want to include as well as the last activity.
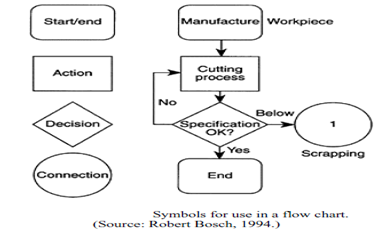
IDENTIFY THE STEPS IN THE PROCESS:
- The output of this step is a list of the detailed process steps.
- A good way to construct such a list is to follow normal transactions through the process and write down on a piece of paper what is happening.
- When a ‘new activity’ is carried out on the transaction you have a new step.
- It is usually necessary to make observations and inquiries where the activities are happening. In this way you will also be able to identify abnormal transactions.
CONSTRUCT THE FLOW CHART:
- Here the correct symbols are used to draw the flow chart. In a QC circle it is normally a good way to construct the flow chart on large pieces of paper (flip chart paper) which are put sequentially side by side on the wall, so that each participant can overview the whole process during the construction.
- With the latest computer packages (Tool Kit, SAS QC etc.), which are very easy to operate, new ways of constructing the flow chart are emerging.
- The text on the flow chart should be short and clear for the people involved in the process. For each step describe what, who and where.
- The people involved in the construction should include those who carry out the work of the process, the internal suppliers and customers, the supervisor of the process and a facilitator.
- The facilitator is a person specifically trained in construction of flow charts.
- Besides drawing the flow chart the facilitator’s job is to secure that all the participants are active in discussing the flow.
- An important issue to discuss during the construction is the measurement issue.
- Discuss what is important for the internal suppliers, the process and the customers (internal as well as external customers) and what is possible to measure.
- But remember: Before trying to control everything, find out what is important.