Plan
Introduction:
The Plan phase consists of two main elements—deciding on the quality goals and policies and design of the quality plans. When deciding on the goals and policies management should have the four sides of the TQM pyramid as a reference. The goals and policies act as a picture (a vision) showing where the company wants to be (the goal of the journey). Planning is the process of designing the detailed plans for quality improvements, i.e. the road map to follow on the quality journey.
PDCA model for implementation:
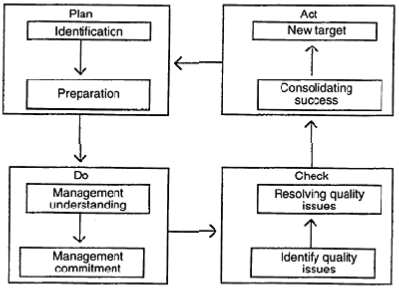
The practical method of identifying the basic problems affecting the company’s activities was applied. An initial survey of all head office (Mitcham) personnel revealed the three main areas for improvement as being:
1. Accountability
2. Communication
3. Quality awareness.
According to the pyramid principle, there are four principles that govern the basic philosophy of TQM:
1. customer focus;
2. continuous improvement;
3. focus on facts;
4. everybody’s participation.
To counter the scepticism detected in some quarters, the potential results of a successful
TQM process was continually stressed in steering group meetings:
1. reduction in wastage;
2. process control improves;
3. company morale gets better.
- The challenge of TQM implementation is very much dependent on the commitment and will of the company’s senior management to carry it through.
- The company had embarked on its road to quality voluntarily whilst in a healthy state.
- However, the subsequent failure of its senior management, particularly the managing director, to adopt the objective and methodology of the quality improvement programme at all times eventually weakened the company’s ability to deal effectively with the pressure of competition and downturn in financial performance when the effects of recession worsened.