←
Automobile Engineering
Distributorless Ignition System (Dis)
Introduction:
Distributorless ignition outputs to the spark plugs without using a distributor. Distributorless ignition uses a special type of ignition coil, which outputs to the spark plugs without the need for a high-tension distributor.
Basic Principle of DIS:
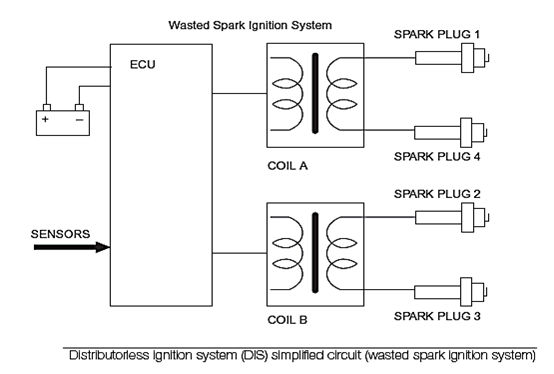
-
The basic principle is that of the ‘lost spark’. The distribution of the spark is achieved by using two double-ended coils, which are fired alternately by the ECU.
- The timing is determined by a crankshaft speed and position sensor as well as a load (MAP) sensor and other corrections such as engine temperature.
- When one of the coils is fired a spark is delivered to two engine cylinders, either 1 and 4 or 2 and 3.
- The spark delivered to the cylinder on the compression stroke will ignite the mixture as normal.
- The spark produced in the other cylinder will have no effect, as this cylinder will be just completing its exhaust stroke. Because of the low compression, and the exhaust gas in the lost spark cylinder, the voltage used for the spark to jump the gap is only about 3 kV.
- The spark produced in the compression cylinder is therefore not affected. An interesting point here is that the spark on one of the cylinders will jump from the earth electrode to the spark plug center.
Inductive sensor
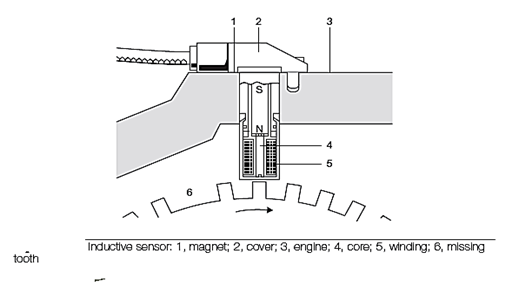
- The crankshaft position sensor is similar in operation to the one described in the fuel section. It is an inductive sensor and is positioned against the front of the flywheel or against a reluctor wheel just behind the front crankshaft pulley.
- The tooth pattern usually consists of 35 teeth.
- These are spaced at 10° intervals with a gap where the 36th tooth would be. The missing tooth is positioned at 90° BTDC for numbers 1 and 4 cylinders.
- This reference position is placed a fixed number of degrees BTDC, to allow the timing or ignition point to be calculated as a fixed angle after the reference mark.
- The primary winding is supplied with battery voltage to a center terminal. The appropriate half of the winding is then switched to earth in the module.
- The high-tension windings are separate and are specific to cylinders 1 and 4 or 2 and 3 (or as appropriate if a six-cylinder engine