Decision Making
The decision-making tasks are usually characterized by a tremendous variety of data and available knowledge, different requirements and constraints, and a dynamically changing environment, which make the use of neural networks quite appropriate. For example, a decision-making system might require taking into account exact data, fuzzy data, and fuzzy rules and membership functions.
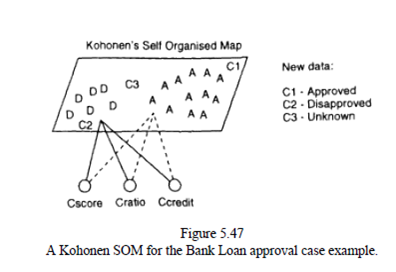
Decision-making may require good explanatory facilities, for which purpose rules extraction from data might be a useful technique. SOM can well be used for visualization of a decision and placing it in regions of similar cases. The applicants Cl, C2, and C3 are "placed" by the network in the areas of "approve, “disapprove," and "not known," respectively.
As another example, a neural can be used to evaluate the possible ranking of a new model of car on the market. The decision is based on training a neural network with ranking data for different models of cars represented by a set of attributes (price, fuel consumption, maintenance, etc.). The system evaluates the ranking if a set of values for the input variables of a new model is entered. The idea of ranking a new model can also be used in the area of design. Which variant to choose when designing an object can be evaluated on thebasis of a set of training examples and a set of constraints introduced to an appropriate neural network architecture. Constraints can be implemented as a second level of knowledge, "above" the network.