What Is Meant By Quality Control
Introduction:
QC is the use of techniques (mainly statistical) to achieve, maintain and try to improve on quality standards of products and services.
Definition:
- Operational techniques and activities aimed both at monitoring a process and eliminating causes of unsatisfactory performance of relevant stages of the quality loop (quality spiral) in order to result in economic effectiveness
- 'The operational techniques and the activities which sustain a quality of product or service that will satisfy given needs.'
QC is therefore the use of techniques (mainly statistical) to achieve, maintain and try to improve on quality standards of products and services. It co-ordinates the links between the following activities:
- Specifications of what is required;
- Designing the products/services required;
- Production/installation/assembly of parts, components, elements of the service/
- Inspection of the product/service package to determine conformance to customer
- Monitoring usage/consumption of product/service to feed back the information product package; specifications; for improvements wherever possible.
Stages:

The concept of control
The concept of control includes all the activities which enable organisations to achieve their objectives efficiently and economically. It is an ongoing process and based on continuously trying to rectify, improve and introduce new concepts. There are three types of control which can be recognized:
(i) Irregular control: Spasmodic approaches to controlling quality (e.g. when a customer complains);
(ii) Routine control: Regular control by carrying out inspections at specific stages of the process of providing goods/services;
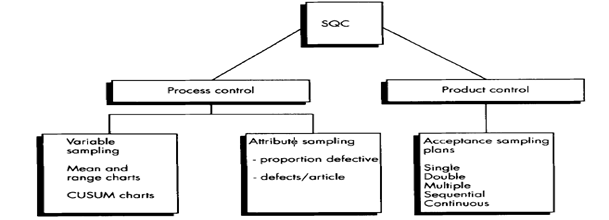
Fig: Various types of Statistical Quality Control techniques
(iii) Scientific control:Control through measurement and analysis using statistical sampling theory. This more or less controls the process (e.g. a repetitive production process)