What Is Tpm?
Introduction:
Maintenance, similarly to a large number of other activities, has been conducted in an ad-hoc manner in most manufacturing organisations. Total Quality Management is aimed at satisfying customer requirements. Total Preventative Maintenance is a continuous improvement activity. To achieve the above objectives, a comprehensive maintenance function has to address planned and unplanned activities, routine and long-term decisions on prevention.
Definition:
Maintenance is the management, control, execution and quality of those activities which will ensure that optimum levels of availability and overall performance of plant are achieved in order to meet business objectives.
Objectives:
To provide flexible and capable processes, a sound maintenance policy should cover the following objectives
1 Ability to extend the useful life of assets (buildings, equipment, site, etc.);
2 Assure the optimum availability of installed equipment for production (or service) and to obtain the maximum possible return on investment;
3 Ensure operational readiness at all times of all equipment required for emergency use, such as standby, firefighting and rescue units;
4 Ensure the safety of personnel using the machinery and equipment.
Terotechnology: 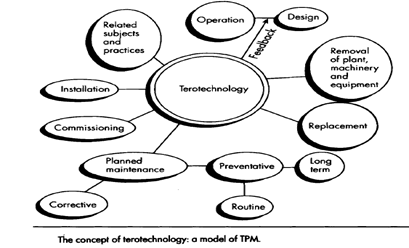
Terotechnology is concerned with the application of managerial, financial, engineering and other skills to extend the operational life of, and increase the efficiency of, equipment and machinery.
- This comprehensive view of TPM suggests that a history of process selection, implementation and performance monitoring has to be made available so that important activities such as operations and design can help meet customer requirement satisfactorily.
- This model reflects the need to have wider involvement in the decision-making process on capital equipment investment and also to have knowledge workers who are responsible for the selection, implementation, operation and control of the process equipment in question.
Structure of a Total Preventative Maintenance programme
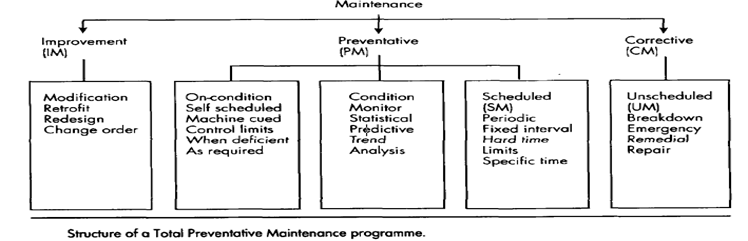
Total Preventative Maintenance in the context of TQM has therefore got to address various aspects of process operations, not just the maintenance engineering angle. A typical TPM programme should include an aspect of Corrective Maintenance (CM), an aspect of Preventative Maintenance (PM) and an aspect of Improvement Maintenance (IM).