Just In Time
Introduction:
“Just in time” is the philosophy which is used toimplement improvement plans quickly and effectively, and to open the door for creativeness and progress. Table presents the main benefits of commonly used lean manufacturing techniques.
JIT/Pull Production System
1. In lean manufacturing, we design operations to respond to the ever-changing requirements of customers by responding to the pull, or demand, of customers.
2. This concept contradicts the traditional batch-and-queue manufacturing approach, facilitates the planning for delivery of products to customers, and stabilizes the demand, especially when customers become confident that they can get what they want when they want it. Thus, a pull system relies on customer demand.
3. A pull scheduling system emphasizes replenishment of what has been consumed or producing only what is needed by customers.
4. A pull system typically uses some type of visual signal, such as an empty box, an open space, or a flashing light to initiate the part-replenishment process.
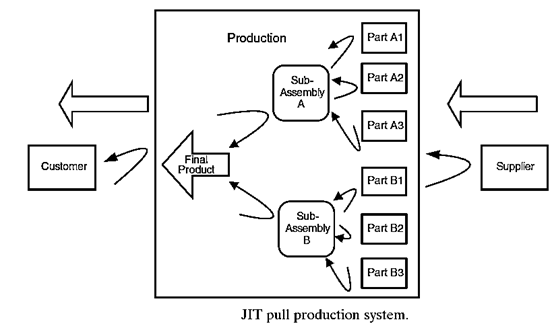
5. A pull system will control and balance the resources required to produce a product and is effective in reducing non value- added activities.
6. In a pull production system, just-in-time (JIT) is a philosophy that strives to reduce sources of waste in manufacturing by emphasizing the production of the right part in the right place at the right time.
7. The idea is to produce or order only the parts that are needed to complete the finished products and to time their arrival at the assembly site. The basic elements of JIT were developed at Toyota in the 1950s by Taiichi Ohno and became known as the Toyota Production System.
8. Before implementing JIT in Toyota, there were a lot of manufacturing defects in the existing system, including inventory problems, product defects, increasing costs, large lot production, and delivery delays. Driven by the demand from customers, the subassemblies and parts required for final assembly are pulled in small batches from the supplying work centers whenever they are needed. Kanban is the key lean technique
9. JIT is expected to improve profits and return on investment by reducing inventory levels and reducing production and delivery lead times.
10. It is particularly beneficial in repetitive manufacturing processes in which the same products and components are produced over and over again.
JIT requirements:
The main requirements for establishing a JIT production environment that integrates key lean techniques include the following:
a) Creating a balanced workload on all workstations through uniform and stable production plan for daily production.
b) Reducing setup and changeover time.
c) Reducing order and production lot size. Reducing the production lot size is related directly to reducing setup times, since it allows the production of smaller lots
d) Reducing production and supply lead times.
e) Management support, supply chain management, and labor involvement.
f) Plant layout with a cellular flow, minimal travel, and clear signaling.
g) Effective production planning and inventory control with MRP.